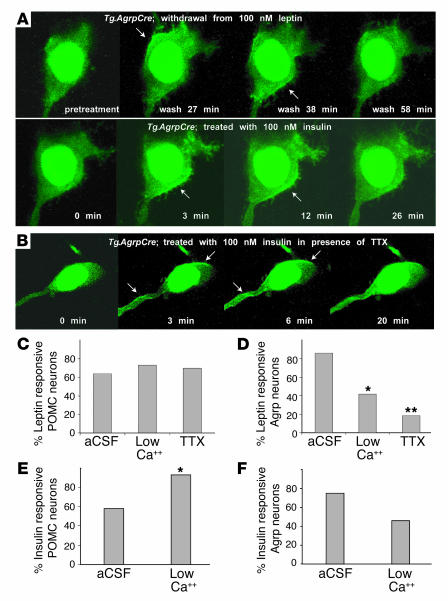
Figure 4.
PI3K regulation by insulin in Agrp neurons and effects of synaptic inhibitors in POMC and Agrp neurons. (A) In Agrp neurons, leptin withdrawal has the same effect as insulin addition; both treatments stimulate membrane localization of the PI3K reporter protein. The example shown represents the same neuron in which a slice preincubated with 100 nM leptin for 60 minutes was then perfused with aCSF; during this time the PI3K reporter protein exhibited initial membrane localization followed by a return to the cytoplasm by 58 minutes. Addition of 100 nM insulin then triggered membrane localization again. In other experiments, 100 nM insulin was observed to cause PI3K activation in Agrp neurons that had not previously been exposed to leptin. Arrows indicate membrane localization. (B) Example of the same experiment as in A but carried out in the presence of 1 μM TTX (which blocked the previous response to leptin withdrawal). (C and D) Percentage of POMC (C) and Agrp (D) neurons responsive to leptin with (aCSF) or without (low Ca++ or TTX) synaptic transmission. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 as determined by χ2 analysis. (E and F) Percentage of POMC (E) and Agrp (F) neurons responsive to insulin with (aCSF) or without (low Ca++) synaptic transmission.