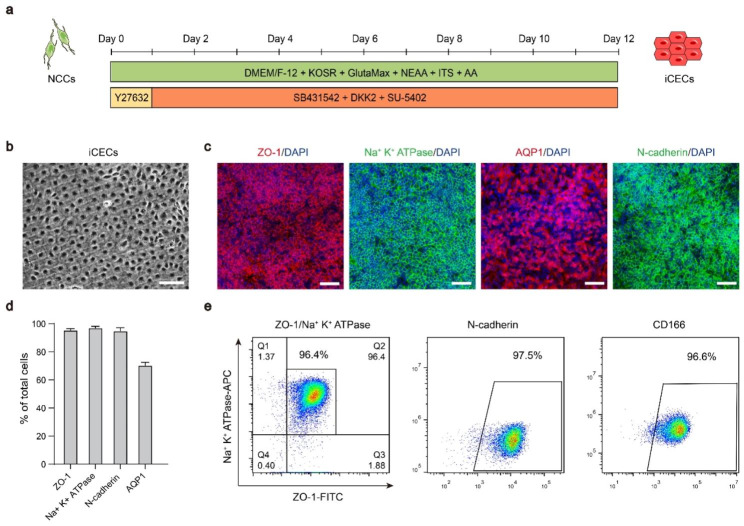
Fig. 2.
Differentiation of hESC-derived NCCs into corneal endothelial cells. a Schematic illustration of the differentiation conditions used to generate corneal endothelial cells from NCCs. b The hexagonal morphology of iCECs differentiated from hESC-derived NCCs. Scale bar: 50 μm. c Immunofluorescence staining showing that iCECs expressed ZO-1, Na+ K+ ATPase, AQP1 and N-cadherin. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bars: 50 μm. d Quantification of the percentage of ZO-1+, Na+ K+ ATPase+, AQP1 + and N-cadherin + cells at day 24 of differentiation. e Flow cytometry analysis of ZO-1/Na+ K+ ATPase, N-cadherin and CD166 expression in iCECs. n = 3