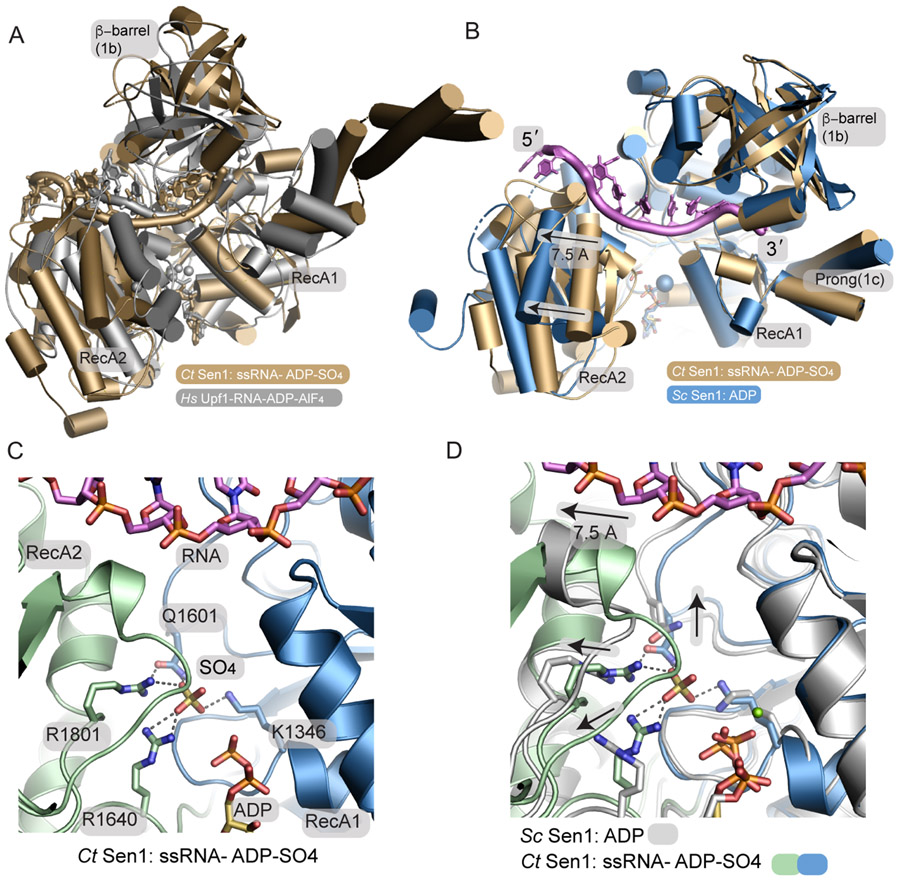
Figure 3. A phosphate sensor is a lynchpin in the Sen1 power stroke.
(A) Structural superposition of the Sen1Hel–RNA–ADP–SO4 complex (tan) with the HsUpf1-RNA-ADP-AlF4 complex (grey).
(B) Structural superposition of the Sen1-RNA-ADP-S04 complex with ScSen1-ADP-Mg2+ complex, RSCB:5MZN. Close superposition of the RecA1 domains is observed. A 7.5 Å translocation is coincident with phosphate release. The blue sphere marks the position of Mg2+ in the ScSen1 -ADP-Mg2+ complex.
(C) Sen1 active site. Four residues from the RecA1 and RecA2 domains bind SO4, a mimic of the hydrolyzed phosphate prior to phosphate release.
(D) Active site structural superposition of ScSen1-ADP and CtSen1-RNA-ADP-SO4 complexes colored as indicated. Arrows show structural rearrangements of conserved gamma-phosphate sensing residues upon phosphate (SO4 mimic) release.