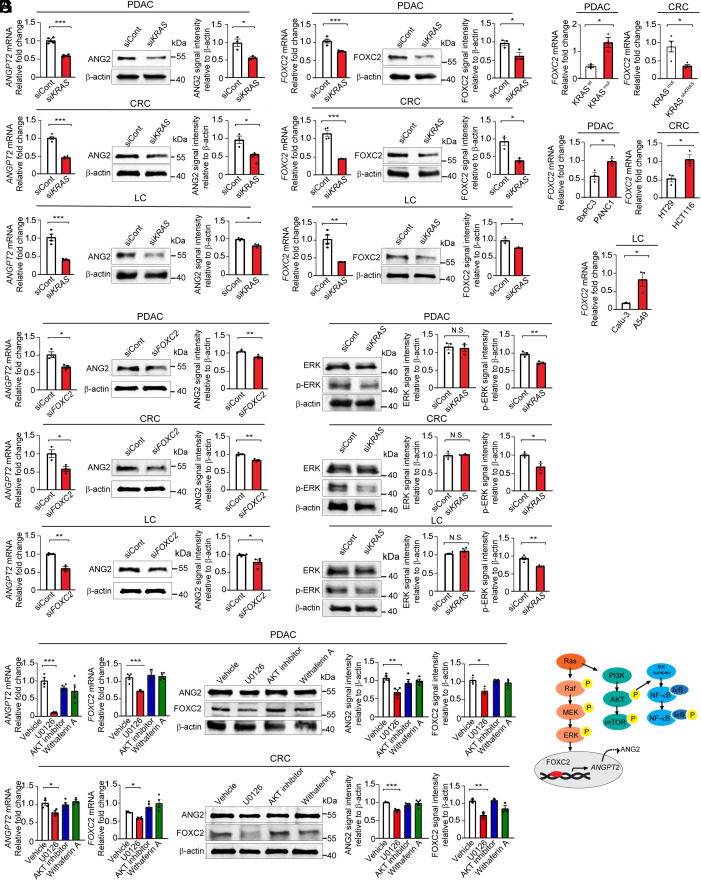
Fig. 3.
KRAS mutation in tumors regulates ANG2 and FOXC2 expression through ERK signaling. (A) Angiopoietin 2 mRNA and protein levels in siKRAS transfected PANC1 PDAC, HCT116 CRC, and A549 lung tumor cell lines (n = 3 to 4 samples per group). (B) FOXC2 mRNA and protein levels in siKRAS transfected PANC1 PDAC, HCT116 CRC, and A549 lung tumor cell lines (n = 3 to 4 samples per group). (C) FOXC2 mRNA levels in BxPC3 WT and BxPC3 KRAS mutant PDAC tumors, HCT116 KRAS mutant and HCT116 shKRAS tumors, BxPC3 and PANC1 PDAC tumors, HT29 and HCT116 CRC tumors, and Calu-3 and A549 lung tumors (n = 3 samples per group). (D) Angiopoietin 2 mRNA and protein levels in siFOXC2 transfected PANC1 PDAC, HCT116 CRC, and A549 lung tumor cell lines (n = 3 samples per group). (E) ERK and phosphorylated-ERK protein levels in siKRAS transfected PANC1 PDAC, HCT116 CRC, and A549 lung tumor cell lines (n = 3 samples per group). (F) Angiopoietin 2 and FOXC2 mRNA and protein levels in PANC1 PDAC and HCT116 CRC tumor cell lines treated with vehicle, U0126, AKT inhibitor, and withaferin A (n = 3 to 4 per group). (G) Schematic diagram showing KRAS–ERK–FOXC2–ANG2 axis. All data represent mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using two-sided unpaired t tests (A–E) and one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison tests (F). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. N.S., not significant. P-ERK, phosphorylated-ERK. PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; CRC, colorectal carcinoma; LC, lung cancer.