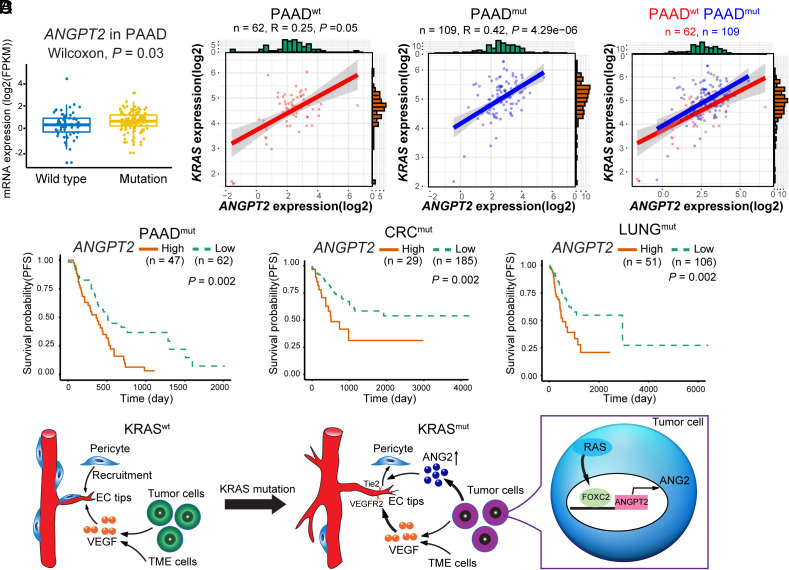
Fig. 8.
Correlation, survivals, and schematic diagram of KRAS mutant tumor–induced anti-VEGF resistance mechanisms. (A) ANGPT2 expression levels in KRAS wt and mutant PDAC patients (PAAD, n = 61 vs. 109, P = 0.003). (B) Correlation of ANGPT2 and KRAS expression in KRAS wt (n = 62, P = 0.05) and mutant (n = 109, P = 4.29e-06) PDAC patients. (C) Kaplan–Meier survival of ANGPT2-high vs. ANGPT2-low PAAD (n = 47 vs. 62, P = 0.002); CRC (n = 29 vs. 185, P = 0.002); and LUAD (n = 51 vs. 106, P = 0.002) of KRAS mutant cases. (D) Schematic diagram of KRAS mutant tumors in promoting pericyte-loss tumor vasculatures. In KRAS wt tumors, tumor- and the TME-derived VEGF promotes tumor angiogenesis, and pericytes are recruited to coat tumor vessels. In contrast, KRAS mutant tumors generate a pericyte-impaired phenotype by increasing tumor-derived ANG2 through the RAS–FOXC2–ANG2 axis, leading to accelerated angiogenesis by sustainable VEGF access to endothelial cells. PAAD, pancreatic cancer; CRC, colorectal cancer; LUNG, lung cancer