Figure 2. EMBOW directly interacts with WDR5 via the WIN site.
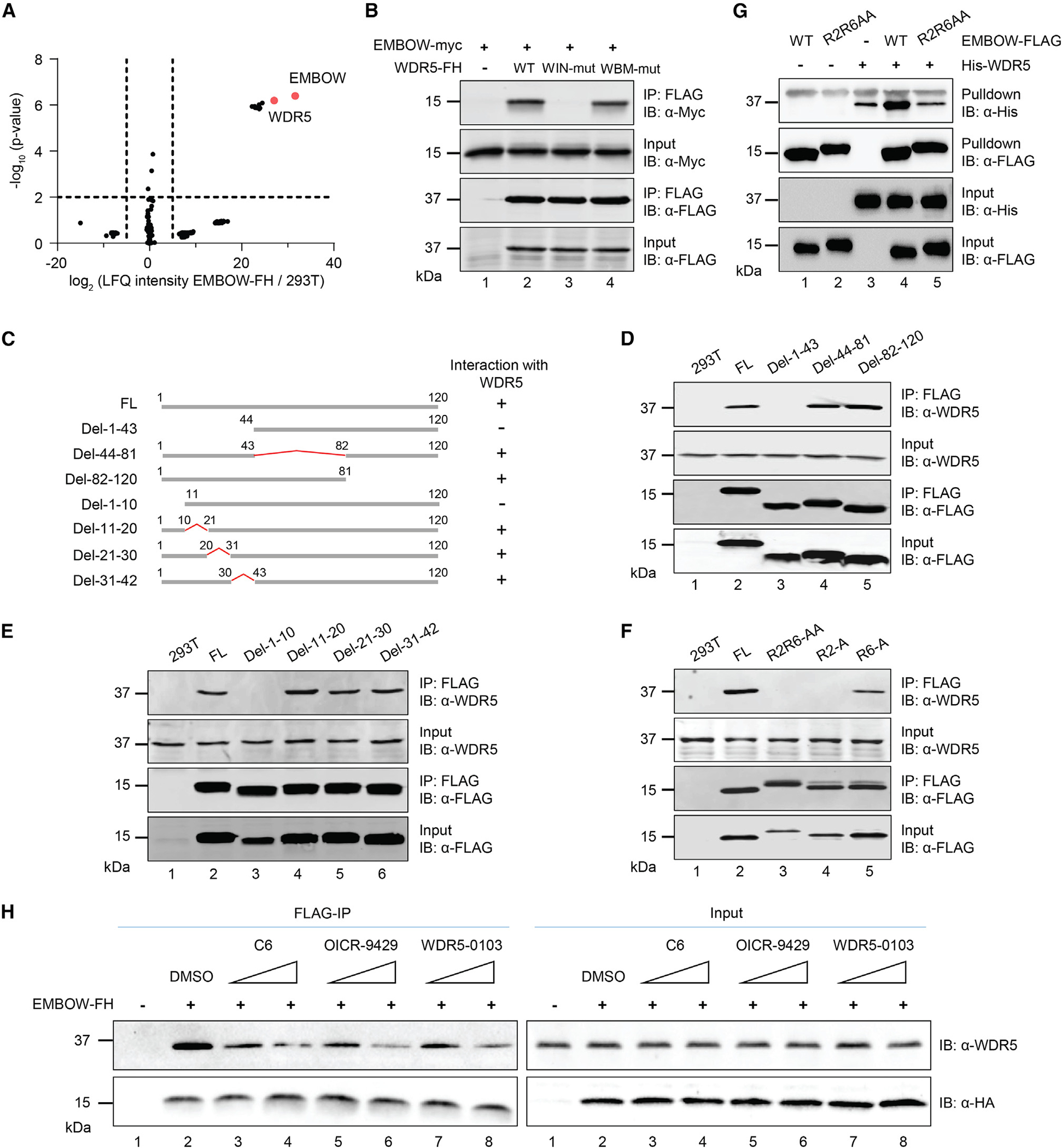
(A) Volcano plot of quantitative proteomics (N = 3 biologically independent experiments) of anti-FLAG pull-down from nuclear lysates of HEK293T cells transiently overexpressing EMBOW-FLAG-HA (EMBOW-FH) or parental (293T) HEK293T. Two-sample p value was calculated using Perseus. For complete quantitative proteomics results, see Table S4.
(B) HEK293T cells were transfected with EMBOW-myc only, or co-transfected with EMBOW-myc and wild-type (WT), or WIN site mutated (WIN-mut), or WBM site mutated WDR5-FH (WBM-mut), followed by IP and IB. Data are representative of three biological replicates.
(C) Schematic representation of full-length (FL) and deletion (del) mutant EMBOW constructs, with amino acid residues numbered above. WDR5 association status of each construct is indicated on the right.
(D–F) HEK293T cells were transfected with EMBOW full-length (FL) or mutants (listed at top), followed by IP and IB. Data are representative of three biological replicates.
(G) His-WDR5, wild-type (WT), or R2R6-to-AA mutated (R2R6AA) EMBOW-FLAG were purified from E. coli, followed by in vitro FLAG pull-down and IB. A nonspecific upper band appears in the anti-His IB channel. Data are representative of three biological replicates.
(H) HEK293T cells were transfected with EMBOW-FH or mock transfection, and FLAG-IP was performed in the absence (DMSO) or presence of WDR5 WIN-site inhibitors C6 (0.5 or 5 μM), OICR-9429 (0.5 or 5 μM), or WDR5-0103 (5 or 50 μM), followed by IB. Data are representative of three biological replicates.
