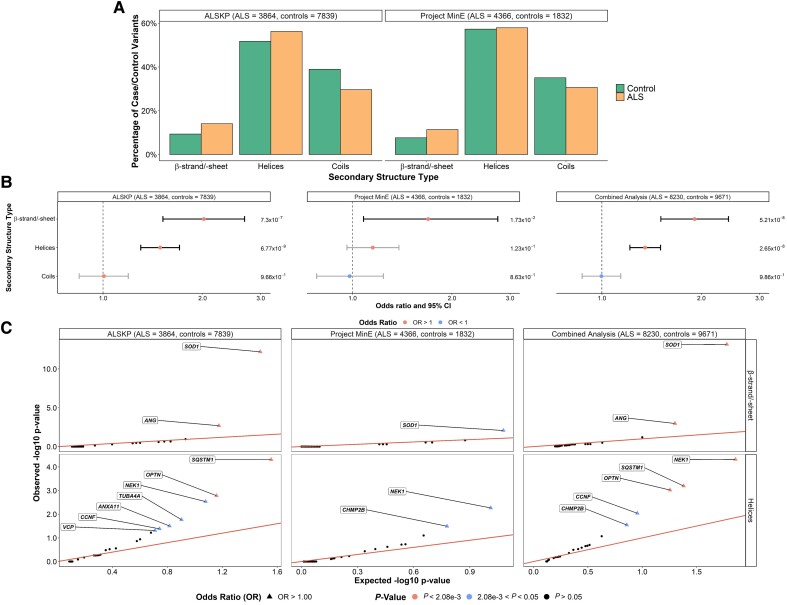
Figure 2.
Secondary structure types at which rare missense variants were identified across 24 ALS-associated genes. (A) Secondary structure types were obtained using the AlphaFold predicted structures and DSSP (dictionary of protein secondary structure) program for all residues at which variants of interest were observed in the ALS Knowledge Portal (ALSKP) and Project MinE ALS sequencing consortium. Secondary structure types were binned based on the following: β-strand/-sheet includes β-strands and β-sheets; helices includes 310-helices, α-helices, π-helices and polyproline II helices; and coils includes loops, bends and turns. (B) Enrichment analyses were performed using Fisher’s exact testing to compare the number of variants carried by individuals with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and controls at residues of each secondary structure type in the ALSKP and Project MinE datasets, followed by a Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel (CMH) test. Significance was measured at an alpha-level of 0.05. (C) Quantile-quantile plots of rare variants of interest identified across 24 ALS-associated genes in ALS case-control sequencing datasets, defined by their secondary structure type. The secondary structure types significantly enriched for variants of interest in the individuals with ALS compared to the controls were further analysed to determine which genes were driving the enrichment of the features using Fisher’s exact testing. Enrichment of variants in β-strands/-sheets was driven by SOD1 (ALSKP, P = 6.26 × 10−13; Project MinE, P = 8.38 × 10−3; combined analysis, P = 6.97 × 10−14) and ANG (ALSKP, P = 2.04 × 10−3; combined analysis, P = 1.05 × 10−3). Enrichment of variants in helices was driven by NEK1 (ALSKP, P = 2.92 × 10−3; Project MinE, P = 5.43 × 10−3; combined analysis, P = 4.81 × 10−5), SQSTM1 (ALSKP, P = 4.92 × 10−5; combined analysis, P = 6.41 × 10−4); and OPTN (ALSKP, P = 1.65 × 10−3; Project MinE, P = 5.43 × 10−3; combined analysis, P = 9.52 × 10−4). An alpha-level of 2.08 × 10−3 was considered significant following Bonferroni correction accounting for the 24 genes analysed.