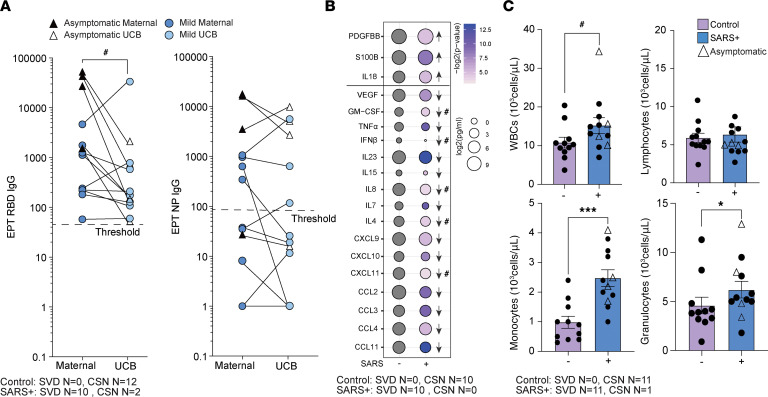
Figure 1. Maternal SARS infection alters frequency of immune cells and immune mediators.
(A) Maternal and UCB anti-RBD (left) and anti-NP (right) EPTs. N = 12/group. (B) Bubble plot comparing UCB plasma immune mediators from control and maternal SARS+ group. Size represents analyte concentration (pg/mL), whereas color represents statistical significance. N = 10/group. (C) UCB complete blood cell counts, including white blood cell (top left), lymphocyte (top right), monocyte (bottom left), and granulocyte (bottom right) proportions from control and maternal SARS+ groups. N = 11 for controls and N = 12 for the SARS+ group. Group differences between data sets normally distributed were tested using an unpaired t test (for data sets with equal variances) or an unpaired t test with Welch’s correction (for cases with unequal variances). Data sets not normally distributed were subjected to nonparametric Mann-Whitney test. Error bars represent the data mean ± SEM. (#P < 0.1, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.0001.) SVD, standard vaginal delivery; CSN, cesarean section.