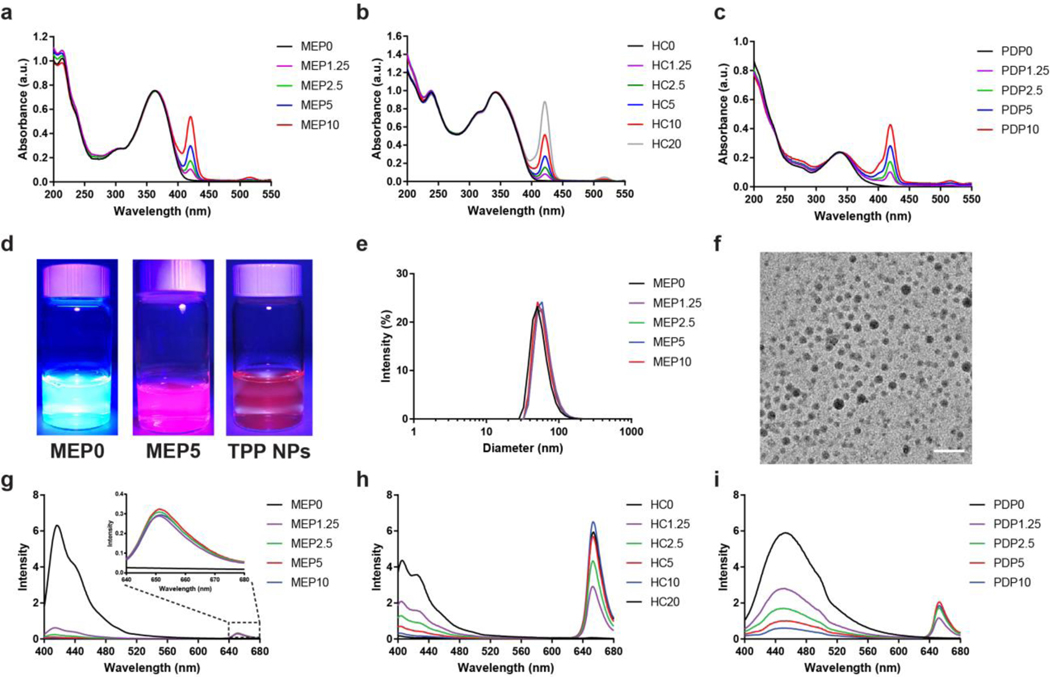
Figure 2.
Characterization and optimal TPP doping percentage in semiconducting polymer nanoparticles (SPNs). UV-VIS spectra of (a) MEP, (b) HC, and (c) PDP photosensitizer doped SPNs. The number following the SPs abbreviation indicates TPP doping percentage weight fraction relative to the respective SPs during formation. (d) Photos comparing representative SPNs, photosensitizer doped SPNs, and TPP NPs under UV light (λex = 395 nm). (e) DLS size distribution and (f) TEM image characterizing the diameter of representative photosensitizer doped SPNs (scale = 100 nm). The optimal TPP doping percentage in (g) MEP, (h) HC, and (i) PDP SPNs was determined by the FL intensity of TPP after exciting the respective SPNs.