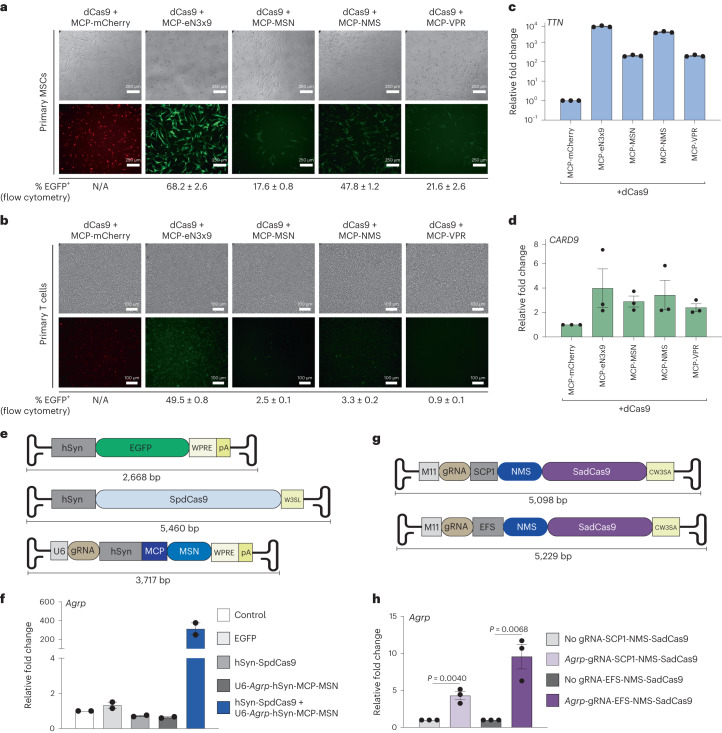
Fig. 6. CRISPR-DREAM components are well tolerated in primary cells and compatible with viral delivery methods.
a,b, Immunofluorescence microscopy showing mCherry/EGFP expression levels in MSCs (a) and human T cells (b) at 72 h after co-transduction of dCas9 in combination with either MCP-mCherry (control), MCP-eN3x9-T2A-EGFP, MCP-MSN-T2A-EGFP, MCP-NMS-T2A-EGFP or MCP-VPR-T2A-EGFP, respectively (white scale bars, 250 μm for MSCs; 100 μm for T cells). MCP-fusion vectors also contain a U6-driven gRNA expression cassette and either a TTN (MSCs) or CARD9 (T cells). c,d, Relative expression of TTN (c) or CARD9 (d) in MSCs and T cells, respectively, 3 d after lentiviral co-transduction using indicated components. e, AAV constructs used for dual-delivery of CRISPR-DREAM components are schematically depicted. The EFGP control vector is shown (top) along with the hSyn promoter-driven SpdCas9 vector (middle), which consists of a modified WPRE/polyA sequence (W3SL). The U6 promoter-driven gRNA expressing vector (bottom) is also shown and also encodes MCP fused to MSN, which is driven by the hSyn promoter. f, Agrp gene activation in mouse primary cortical neurons using the dual AAV8 transduced CRISPR-DREAM system described (in e) at 5 d post-transduction. g, AIO SadCas9-based AAV vectors are schematically depicted. AIO vectors consist of M11 promoter-driven gRNA cassettes and either SCP1 (top) or EFS (bottom) promoter-driven NMS-SadCas9. A modified WPRE/polyA sequence (CW3SA) was used in the AIO vectors. h, Agrp gene activation in mouse primary cortical neurons transduced with AIO AAV vectors (in h) at 5 d post-transduction. Data are the result of 3 biological replicates for c, d and h and 3 biological replicates for f. See the source data for more information. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. P values were determined using unpaired two-sided t-test. N/A, not applicable.