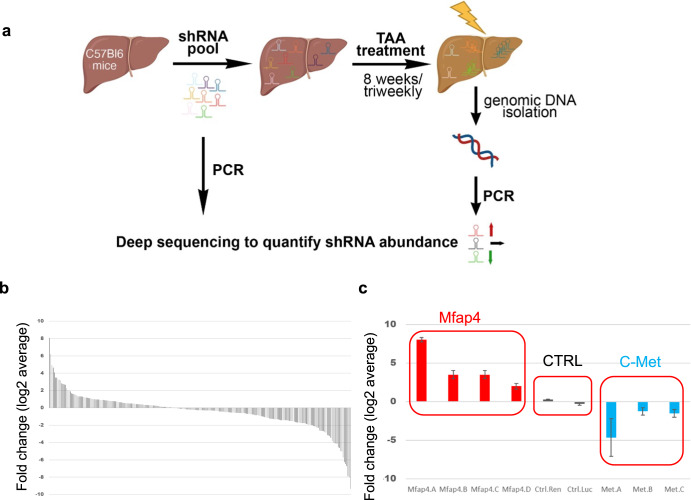
Fig. 1. Functional genetic in vivo RNAi screen to identify therapeutic targets to enhance liver regeneration.
a Outline of the screen. mice were injected with a pool of shRNAs (5 independent mice). After stable integration (~10% of hepatocytes), mice were treated with thioacetamide (TAA) to induce chronic liver damage associated with advanced liver fibrosis. Changes in shRNA abundance are detected by deep sequencing. This figure was created by the author V.I. with BioRender.com. b Representation of log2 fold change for each shRNA (ROMAampl library, 253 shRNAs, shown is the average value of 5 animals). c Functional genetic screen identifies Mfap4 as high confidence candidate (left red square) (zoom-in of (b) is shown). Several independent shRNAs were enriched targeting Mfap4 (left red square). Furthermore, non-targeting control (shNC) shRNAs (middle red square) did not show significant enrichment or depletion, and shRNAs targeting c-Met, an essential receptor for liver regeneration, are depleted (right red square).