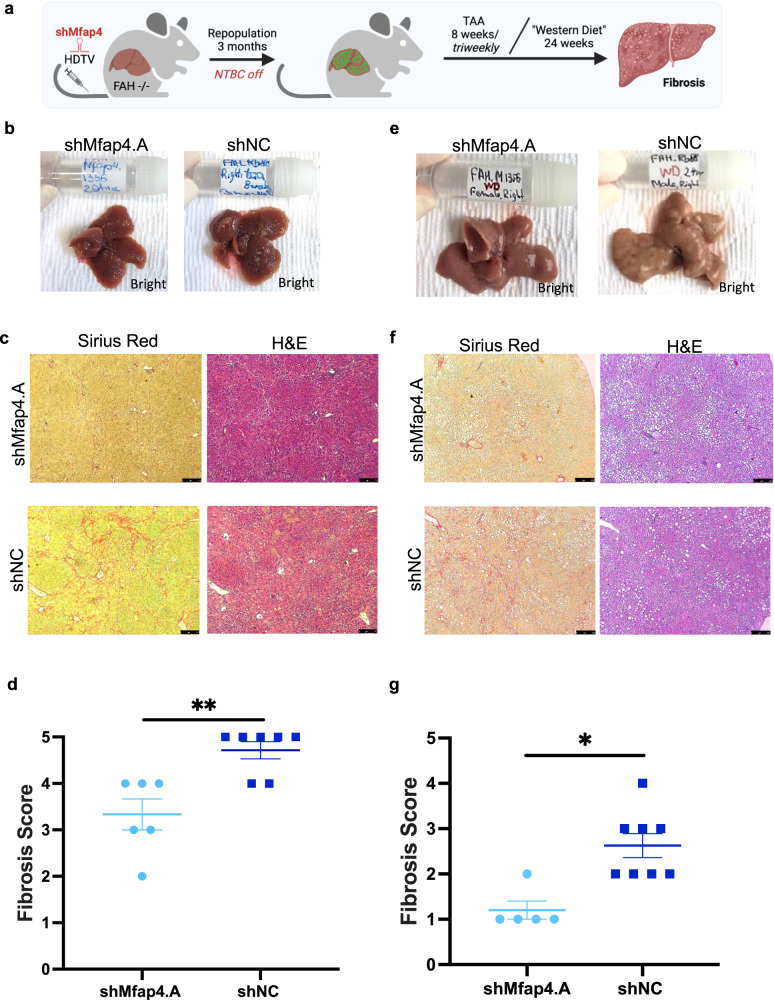
Fig. 4. Mfap4 knockdown attenuates chronic liver damage related liver fibrosis.
a Experimental outline of thioacetamide (TAA) induced chronic liver damage model and “Western Diet” induced NASH model. FAH−/− mice were injected with p/T-FAHIG-shRNA and SB13 constructs. After full liver repopulation, chronic liver damage was induced by repetitive doses of TAA administered intraperitoneal 3 times per week for 8 weeks or mice were exposed to the “Western Diet” (high-fat diet and 60 % fructose) for 24 weeks. Livers were harvested, processed, and analyzed. b Representative macro-photographs of the livers are shown (bright field; shMfap4 n = 6, shNC n = 7). Already macroscopic differences between groups were visible (TAA model). c Left column, Sirius red staining for fibrotic scar tissue of liver sections corresponding to (b). Right column H&E staining of liver sections corresponding to (b) (magnification ×50, representative images are shown, bar = 250 μm; n = 6 per experimental group and n = 7 per control group). d Quantification of (c). Fibrosis score is determined by a certified pathologist, who was blinded regarding the experimental group (each point represents one animal; **p < 0.01). e Representative macro-photographs of the livers are shown (bright field; shMfap4 n = 5, shNC, n = 8). Already macroscopic differences between groups were visible (“Western Diet” model). f Left column, Sirius red staining for fibrotic scar tissue of liver sections corresponding to (e). Right column H&E staining of liver sections corresponding to (e) (magnification ×50, representative images are shown, bar = 250 μm). g Quantification of (f). Fibrosis score is determined by a certified pathologist, who was blinded regarding the experimental group (each point represents one animal; **p < 0.01).