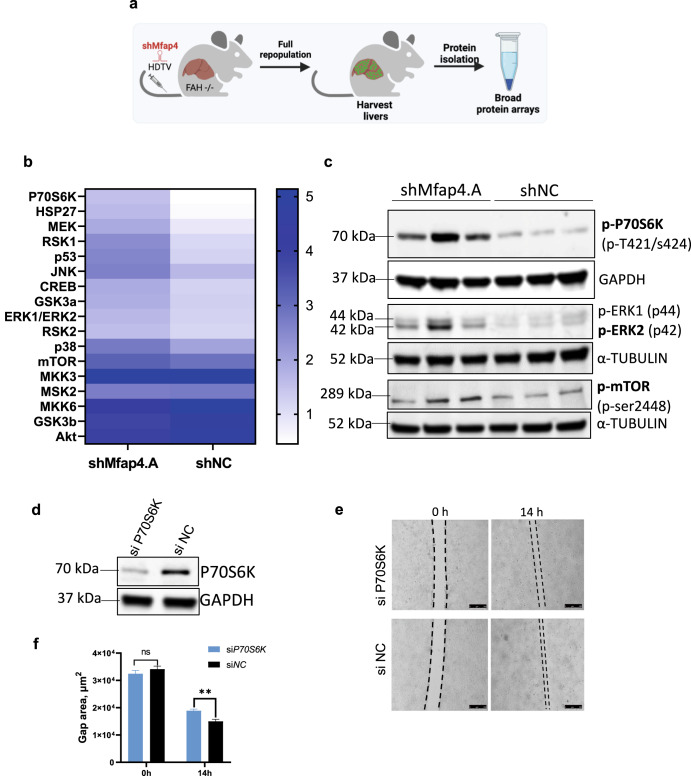
Fig. 6. Knockdown of Mfap4 impacts mTOR and ERK signaling.
a Schematic outline of the experiment. Whole-cell protein extracts from repopulated mouse livers were isolated and analyzed by protein array. b Heat map shows results for phosphorylation specific MAPK pathway protein array. Whole-cell protein extracts from repopulated mouse livers with stable expression of either shMfap4 or shNC were analyzed (shown is the relative signal intensity). c Western blot analysis for the phosphorylation status of P70S6k, ERK1,2, mTOR, corresponding to (b). α-Tubulin or GAPDH serves as a loading control (n = 3). d Knockdown test of P70S6K siRNA pool. Western blot of protein extracts from BNL.CL2 cells with stable shMfap4 expression were treated either with siP70S6k or siNC. GAPDH serves as a loading control (n = 3). e Wound healing under double knockdown conditions. Liver cell line with stable knockdown of Mfap4 was expanded, after that cells were treated with respective siRNAs, and the silicon gasket was removed. Wound healing was monitored. Slower growth and migration were observed in the case of double-knockdown of Mfap4 and p70S6k. f Quantification of (e) is shown (values of wound area in μm2 ± SEM; n = 3; **p < 0.01; ns non-significant).