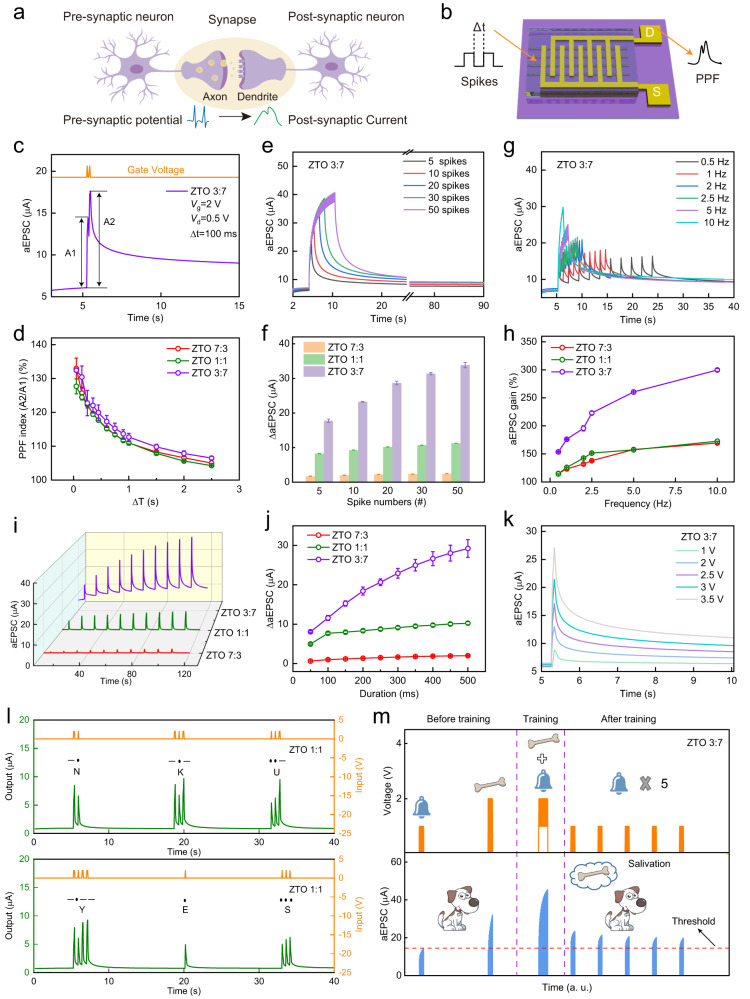
Fig. 3. ZTO-fibers artificial synapses with tunable synaptic plasticity.
a, b Schematic illustration of synaptic signal conduction under a pair of stimuli: biological synapse (a) and ZTO-fibers AS (b). c aEPSC of ZTO-3:7 AS evoked by a pair of spikes. d PPF index versus spike interval for three ZTO ASs with different Zn:Sn molar ratios. e, f aEPSC of ZTO-3:7 AS (e) and ΔaEPSC of three ZTO ASs with different Zn:Sn molar ratios (f) triggered by consecutive spikes with different spike numbers. g aEPSC of ZTO-3:7 AS triggered by consecutive spikes with different spike frequencies. h aEPSC gain versus frequency for three ZTO ASs with different Zn:Sn molar ratios. i, j aEPSC (i) and ΔaEPSC (j) triggered by spikes with different spike duration for three ZTO ASs with different Zn:Sn molar ratios. k aEPSC of ZTO-3:7 AS triggered by spikes with different amplitude. l International Morse code of “NKU” and “YES” realized using ZTO-1:1 AS. m Pavlovian learning behavior realized using ZTO-3:7 AS.