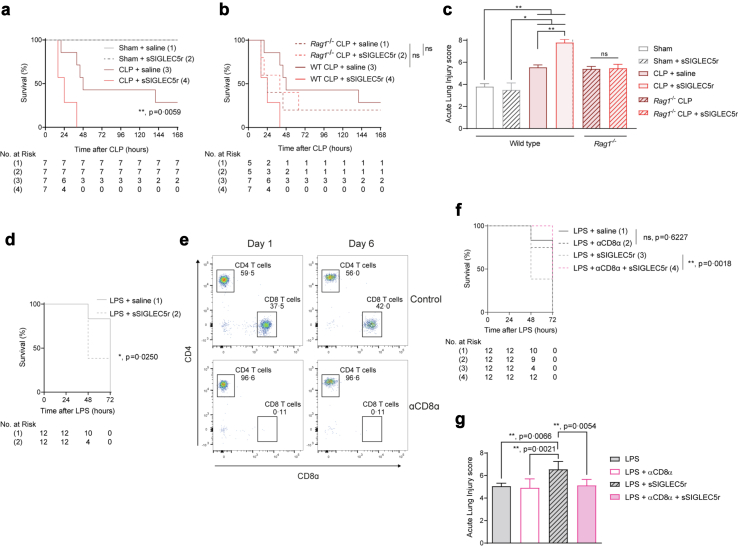
Fig. 4.
SIGLEC5 reduces survival in endotoxemia mouse models in a CD8α-dependent manner. (a) Kaplan–Meier estimation of survival from CLP-mice injected or not with sSIGLEC5r (χ2 = 33.20, p < 0.0001 for all four groups comparison: Sham, Sham + sSIGLEC5r, CLP + saline and CLP + sSIGLEC5r; χ2 = 7.591, p = 0.0059, hazard ratio [HR] CLP plus sSIGLEC5r vs. CLP groups comparison of 8.302; 95% CI, 1.842–37.42) (n = 7 per group). (b) Kaplan–Meier estimation of survival from CLP-WT or CLP-Rag1−/− mice injected or not with sSIGLEC5r (χ2 = 0.064, p = n.s., Hazard ratio [HR] Rag1−/− CLP vs. Rag1−/− CLP + sSIGLEC5 of 0.828, 95% CI, 0.191–3.582) (n = 5 per group in WT mice and n = 7 per group in Rag1−/− mice). (c) Acute lung injury evaluated on Haematoxylin/Eosin-stained lung sections of Sham or CLP-mice in the background wild-type or Rag1−/− injected or not with sSIGLEC5r (n = 7 per group). (d) Kaplan–Meier estimates of survival from mice injected with sSIGLEC5r and/or LPS (χ2 = 5.026, p = 0.0250, HR of 6.019, 95% CI, 1.253–28.91) (n = 12 per group). (e) Flow cytometry-gating strategy for CD4+ and CD8α+ T cells in blood from control and CD8α-depleted mice at day 1 and 6 after injection of a depleting CD8α antibody (20 μg/mice). (f) Kaplan–Meier estimates of survival from mice injected with LPS (20 mg/kg) with or without CD8α depletion (χ = 0.242, p = 0.6227, HR of 0.920, 95% CI, 0.413–2.049) or injected with LPS and sSIGLEC5r with or without CD8α depletion (χ2 = 9.731, p = 0.0018, HR of 14.21, 95% CI, 2.681–75.29) (n = 12 per group). (g) Acute lung injury evaluated on Haematoxylin/Eosin stained lung sections of the endotoxemia mouse model with LPS injection (20 mg/mL), CD8α-depleted or not, and injected or not with sSIGLEC5r (n = 12 per group). (a, b, and d–f) Kaplan–Meier estimation of survival test (∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01). (c and g) Data shown as mean ± SEM. Paired t-test (ns, non-significant; ∗∗p < 0.01).