Figure 5. Conformation of Y-complexes and characterization of orphan Nup densities and linker domains in the double outer ring.
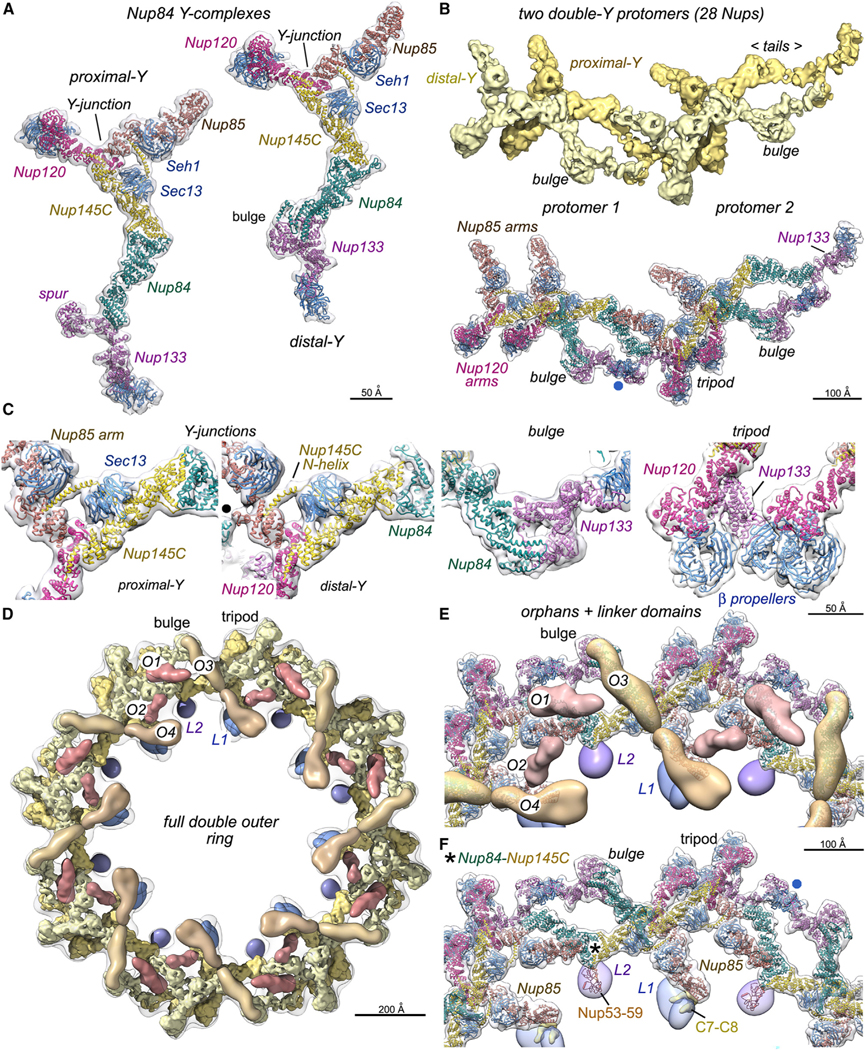
(A) Left: ribbon model for the proximal Nup84 Y-complex oriented vertically. Right: model of the distal Y-complex with the vertical offset that is present in the double ring protomer.
(B) Top: 3D density map with four Nup84 complexes in two protomers of the double outer ring. Bottom: molecular model of two adjacent protomers with notable features labeled. A non-canonical interaction of the distal Nup133 β-propeller with the spur of the proximal Nup133 is marked (blue dot).
(C) Four panels with close-up views of notable regions in Nup84 Y-complexes, including the Y-junction/hub, a non-canonical bulge in the distal Y-complex, and a tripod of membrane-interacting β-propellers. The black dot in panel 2 marks a lateral contact between Nup85 and Nup84 in an adjacent protomer.
(D) Overview of a full double outer ring with putative Nic96 CTDs (O1 and O2; dark brown), possible Nup188–192 orphans (O3 and O4; medium brown), linker domains (L1, dark blue; L2, purple), proximal and distal Y-complexes (gold and light yellow).
(E) A zoomed-in view of the full double outer ring with models of the double Y-protomers and orphans.
(F) A similar view to (E) without orphan Nups; semi-transparent L1 and L2 linker domains reveal their respective footprints on Nup188 in the spoke (above the C7– C8 connectors) and the Nup53–Nup59 heterodimer. A contact site for L2 on the proximal Y-complex is indicated (asterisk) along with a non-canonical interaction of the distal Nup133 β-propeller (blue dot).
