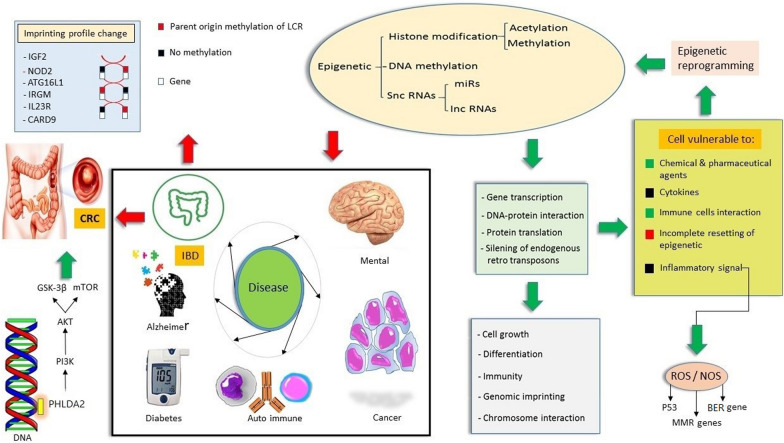
Fig. 1.
Epigenetic plays critical role in multi-factorial disease. Epigenetic changes affect gene transcription, DNA–Protein interaction, Protein translation, and silencing of endogenous retro transposons. Consequently, important functions, such as cell growth, differentiation, immunity, genomic imprinting, and chromosome interaction change and make the cell vulnerable to inflammatory signals, cytokines, and other agents and changes. These cells start epigenetic reprogramming in response to the new environmental changes. IGF2: Insulin-like growth factor II, NOD2: Nucleotide Binding Oligomerization Domain Containing 2, ATG16L1: Autophagy-Related 16-Like 1, IRGM: Immunity-related GTPase family M protein, IL23R: Interleukin 23 Receptor, CARD9: Caspase Recruitment Domain Family Member 9, PHLDA2: Pleckstrin homology like domain family A member 2, CRC: Colorectal cancer, IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease, ROS: Oxidative Redox Stress, NOS: Nitric oxide synthase, MMR, DNA: DNA mismatch repair, BER: base excision-repair