Figure 8.
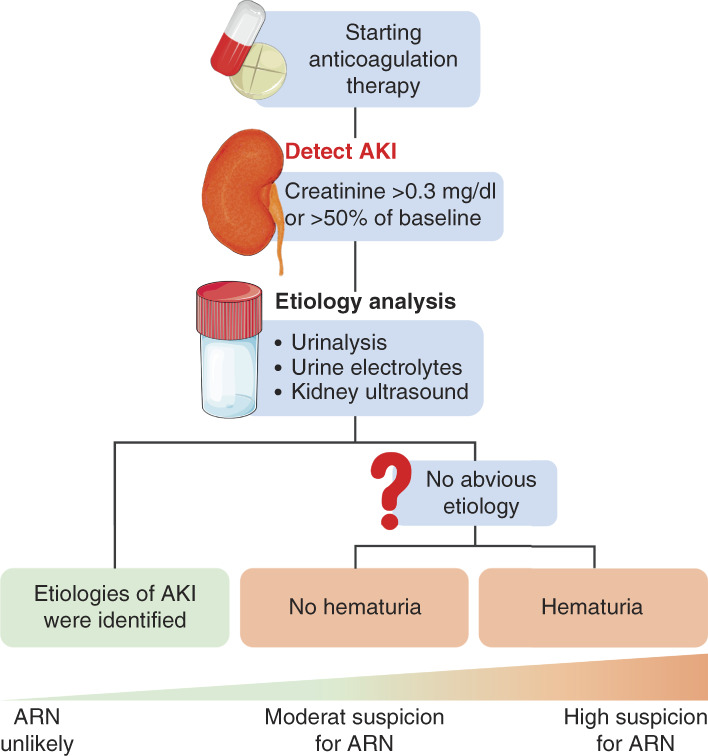
Diagnosis of ARN. When AKI occurs in patients undergoing anticoagulant therapy with an INR >3.0, ARN should be considered. The first diagnosis is to identify the cause of AKI by urinalysis, urine electrolytes, and kidney ultrasound. If the cause of AKI is clear, ARN could be excluded. If the cause of AKI is unclear, further diagnosis is needed to determine whether the patient develops hematuria. ARN is diagnosed if the patient develops hematuria. If the patient does not develop hematuria, the ARN is not fully determined, but the patient is always treated as ARN. ARN, anticoagulation-related nephropathy; INR, international normalized ratio.
