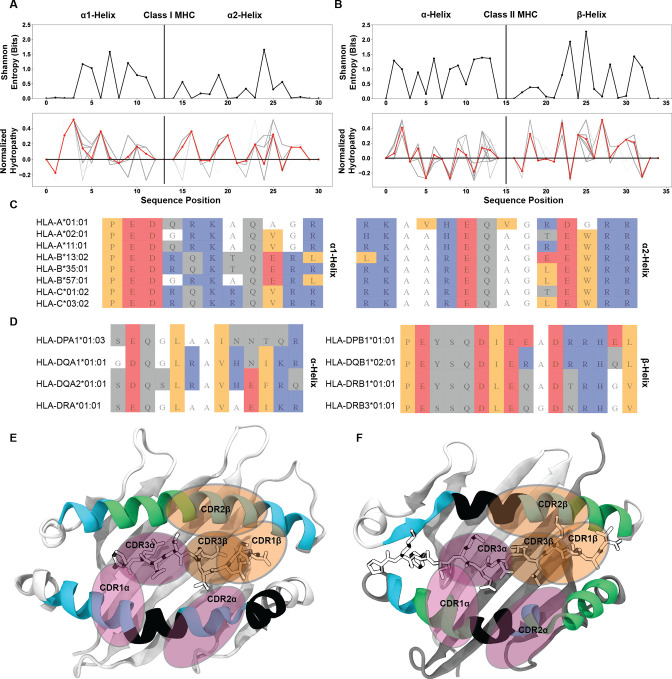
Figure 8. Identification of well conserved regions of low interaction potential finalize a working model for the root cause of canonical TCR-MHC docking orientations.
Position-sensitive Shannon entropy (top) and normalized amino acid hydropathy (bottom) for class I (A) and class II (B) HLA molecules. Red lines in the hydropathy plots indicate an average over all HLA molecules, while gray lines give the position-sensitive biophysical properties of individual molecules. Alignments of class I (C) or class II (D) HLA alleles from a subsampling of parental alleles, colored by biophysical property. Color coding for alignment: grey - hydrophilic, blue - positively charged, red - negatively charged, orange - hydrophobic, white - non-interacting. Renders of class I (E, PDB: 6MTM) and class II (F, PDB: 1J8H) HLA molecules with α-helices colored by interaction potential. Green - regions of high interaction potential, cyan - regions of moderate interaction potential, black - regions of negligible interaction potential. Orange ovals give probable contact regions for TCRβ, while purple ovals give probable contact regions for TCRα, defining canonical docking orientations.