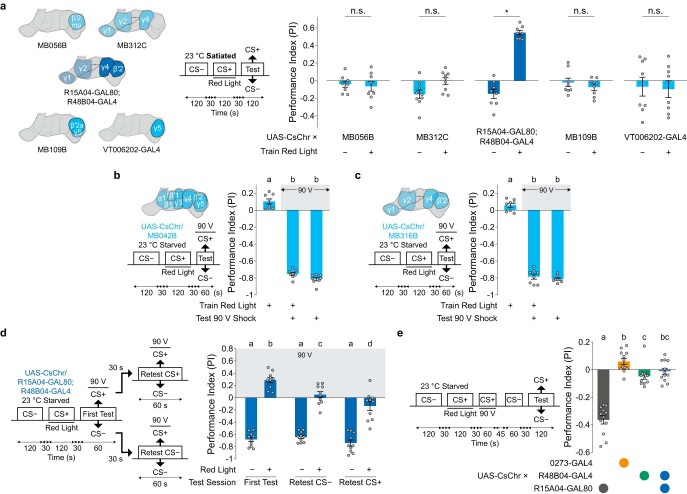
Extended Data Fig. 4. Flies trained with coactivation of sufficient β′2 and γ4 DANs seek reward even after experiencing the CS+ odour with shock.
a, Left: Schematics and protocol. Right: Only training with activation of both β′2 and γ4 DANs paired with an odour leads to substantial conditioned approach (n = 8, MB312C n = 9). Breaks in x-axis demarcate separate experiments. Asterisks indicate significantly different groups (p < 0.05; two-sided unpaired t-test for each genotype with Holm-Šidák’s correction; n.s. = not significant). b, Left: Schematic and protocol. Right: Red-light-trained MB042B flies expressing UAS-CsChr exhibit only minor conditioned approach that is not shock-resistant (n = 8). c, Left: Schematic and protocol. Right: Red-light-trained MB316B flies expressing UAS-CsChr similarly exhibit minor conditioned approach that is not shock-resistant (n = 8). Different letters above bars in b, c indicate significantly different groups (p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA then Tukey’s HSD). d, Left: Consecutive testing protocol. Right: Flies with β′2&γ4 DAN-implanted memories subjected to consecutive testing in the presence of shock continue to approach the electrified CS+ odour irrespective of their first test choice (n = 10). Different letters above bars indicate significantly different groups (p < 0.05; two-way ANOVA then multiple comparisons with Šidák’s correction). Note that not all flies in the Retest CS− groups have necessarily experienced the CS+ during the first test (and vice versa for the Retest CS+ groups). e, Left: Consecutive training protocol. Right: Flies with β′2&γ4 DAN implanted memory and then trained to associate the CS+ with shock continue to approach the reward-predicting CS+ compared with control flies (n = 12). Different letters above bars indicate significantly different groups (p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA then Tukey’s HSD). All data mean ± SEM; dots are individual data points that correspond to independent behavioural experiments. Exact statistical values and comparisons in Supplementary Information.