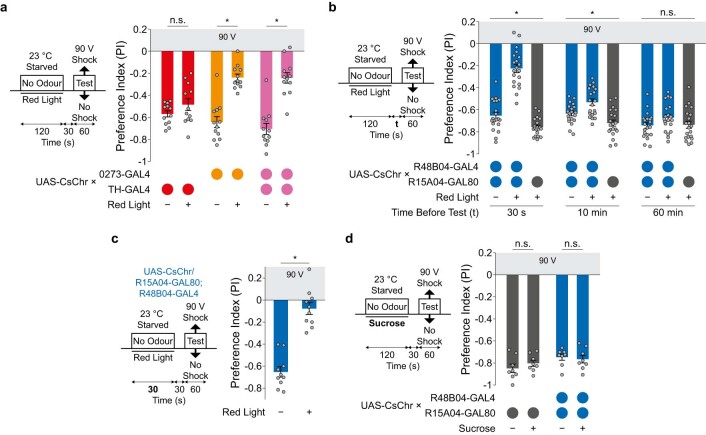
Extended Data Fig. 5. Reward DAN activation impedes subsequent shock avoidance.
a, Left: Protocol. Right: Artificial activation of TH neurons does not affect subsequent naïve shock avoidance, nor does TH neuron coactivation with 0273 neurons restore shock avoidance performance (n = 12; * p < 0.05; two-way ANOVA then multiple comparisons with Šidák’s correction; n.s. = not significant). b, Left: Protocol with variable time t between red light activation and shock avoidance testing. Right: Naïve shock avoidance remains impaired compared with genetic and protocol controls 10 min after β′2&γ4 DAN activation but returns to normal levels by 60 min (n = 20; * p < 0.05; two-way ANOVA then Tukey’s HSD). c, Left: Protocol. Right: Naïve shock avoidance is impaired after β′2&γ4 DANs are activated for just 30 s (n = 10; * p < 0.05; two-sided unpaired t-test). d, Left: Protocol. Right: Sucrose presentation to starved flies for 120 s does not affect subsequent naïve shock avoidance in UAS-CsChr/R15A04-GAL80; R48B04-GAL4 flies or UAS-CsChr/R15A04-GAL80 flies (n = 8; p > 0.05; two-way ANOVA; main effect of treatment: F(1,28) = 104.9, p = 0.66). All data mean ± SEM; dots are individual data points that correspond to independent behavioural experiments. Exact statistical values and comparisons in Supplementary Information.