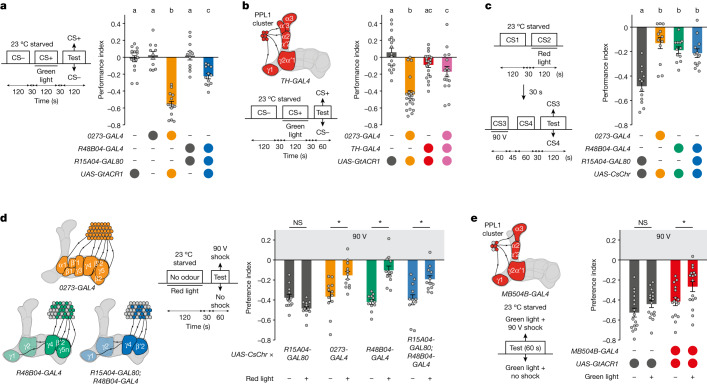
Fig. 3. Reward DANs antagonize aversive DAN function.
a, Left, schematics and protocol. Right, optogenetic silencing of 0273 neurons implants aversive memory for CS+ odour. Silencing β′2&γ4 DANs (R15A04-GAL80; R48B04-GAL4) forms aversive memory with less strength (left to right: n = 16, 11, 14, 11 and 12). b, Left, protocol and schematic of DANs labelled by TH-GAL4 (other labelled neurons not shown) that project from PPL1 to vertical lobe mushroom body compartments. Right, optogenetic silencing of TH-GAL4 DANs alone has no effect, whereas silencing both 0273 neurons and TH-GAL4 neurons largely abrogates aversive memory implanted with 0273-neuron silencing (left to right: n = 18, 21, 21, 16). c, Left, experimental protocol. Right, flies trained with artificial DAN activation do not learn a subsequent shock-paired CS+ as effectively as R15A04-GAL80 controls (n = 12). Different letters above bars in a–c indicate groups that are significantly different from each other (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA then Tukey’s HSD). d, Left, schematics and experimental protocol. Right, flies that experience optogenetic activation in an odourless tube show less subsequent shock avoidance than no-light controls of the same genotype (n = 12). e, Left, schematic and protocol. Right, flies with silenced PPL1 DANs exhibit less shock avoidance than controls (n = 16). d,e, *P < 0.05; two-way ANOVA then multiple comparisons with Šidák’s correction. NS, not significant. Data are mean ± s.e.m.; dots are individual data points that correspond to independent behavioural experiments. Exact statistical values and comparisons are presented in Supplementary Information.