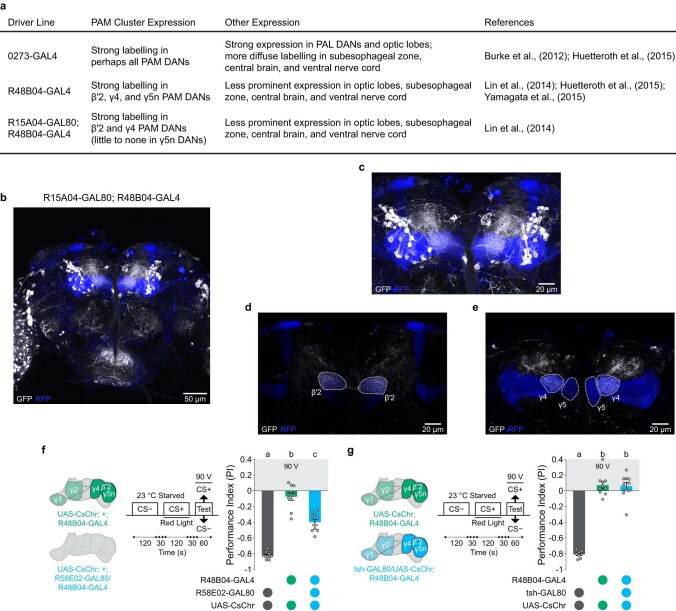
Extended Data Fig. 3. Expression patterns of PAM DAN driver lines that are required for shock-resistant reward seeking.
a, Table summarizing all PAM cluster expression and other expression for each driver line whose artificial activation reinforces shock-resistant reward seeking. References containing images of expression patterns are listed. b, Representative GFP expression (white) driven by R48B04-GAL4 combined with R15A04-GAL80, and the mushroom body (blue) co-labelled with RFP for reference. c, Magnified mushroom body GFP expression driven by R15A04-GAL80; R48B04-GAL4. d, R15A04-GAL80; R48B04-GAL4 drives GFP expression in β′2 DANs (dashed shapes). e, R15A04-GAL80; R48B04-GAL4 also drives GFP expression in γ4 DANs but not γ5 DANs (dashed shapes). The representative images in b, c, d, e are reproduced from source confocal data of one of two brains from ref. 24. f, Left: Schematics and protocol. Right: UAS-CsChr; R48B04-GAL4 flies artificially trained with red light exhibit shock-resistant reward seeking that is impaired by R58E02-GAL80 coexpression (n = 10). g, Left: Schematics and protocol. Right: tsh-GAL80 coexpression did not impair shock-resistant reward seeking driven by UAS-CsChr; R48B04-GAL4 (n = 10, 10, 8). Different letters above bars indicate significantly different groups (p < 0.05; one-way ANOVA then Tukey’s HSD). All data mean ± SEM; dots are individual data points that correspond to independent behavioural experiments. Exact statistical values and comparisons in Supplementary Information.