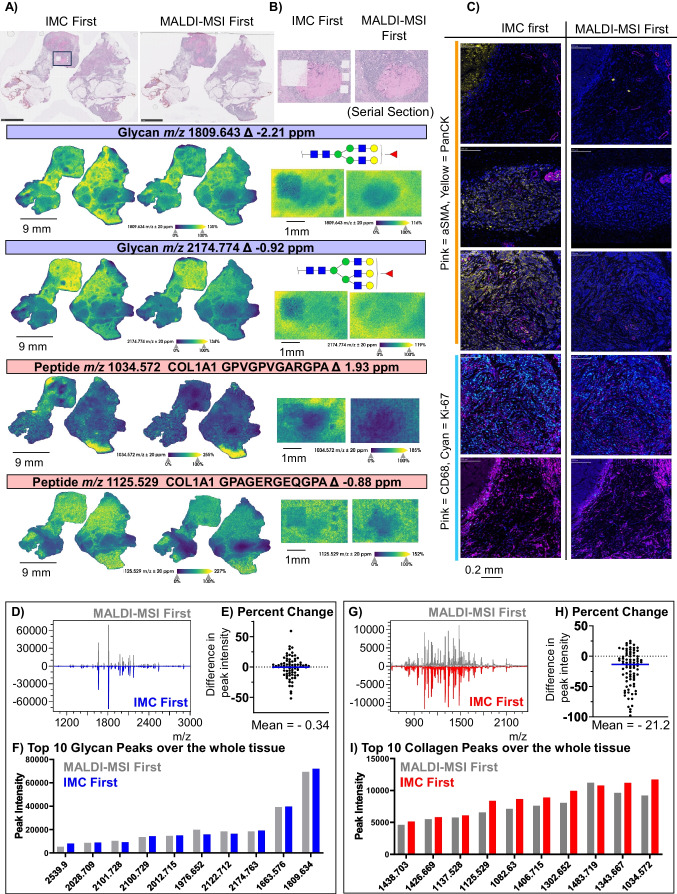
Fig. 3.
Combination of MALDI-MSI and IMC on human breast cancer tissue. A Whole tissue H&E and MALDI-MSI images of breast samples processed by MALDI-MSI first (left column) and IMC first (right column) both taken with 80-µm step size. Images from two N-glycan structures (1809.625 and 2174.763 m/z) are shown followed by two extracellular matrix molecules (1034.572 m/z and 1125.529 m/z). B Magnified H&E and higher resolution (step size of 20 µm) MALDI-MSI images of area analyzed by IMC that shows the spot of tissue ablation from the IMC laser for matched N-glycan/peptide structures from A. C IMC images from slides processed by IMC first (left column) and MALDI-MSI first (right column). Markers visualized are labeled by row. D Comparison of N-glycan spectra showing MALDI-MSI first on top and IMC first flipped on the bottom. E Differences in peak intensity relative to MALDI-MSI first. F Top 10 peaks of highest intensity in IMC first are compared for N-glycans. G Comparisons of the whole spectra collagens. H The percent difference in peak intensity for a subset of selected peaks with respect to MALDI-MSI first. I Ten highest intensity peaks ranked by IMC first compared to intensities of MALDI-MSI first. (D–I are measured from the whole tissue)