Fig. 2.
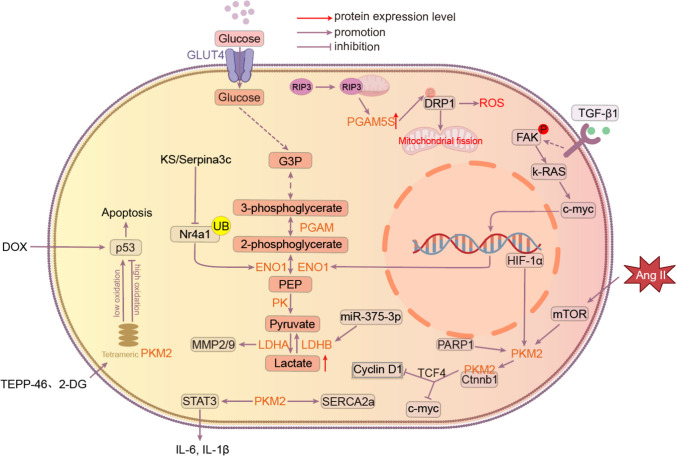
KS/Serpina3c inhibits transcriptional activation of ENO1 by regulating the acetylation of Nr4a1, thereby reducing glycolytic overactivation to prevent fibrosis after ischemia/reperfusion injury. In the failing heart, PKM2 tetramers bind directly to p53 and inhibit p53 transcriptional activity and apoptosis in the high oxidative state, thereby alleviating the progression of heart failure. However, they are enhanced in the low-oxidized state, and the small molecules TEPP-46 and 2-DG can promote PKM2 tetramer formation. When RIP3 translocates to mitochondria, it induces elevated PGAM5S expression, promotes Ser637 dephosphorylation on Drp-1, and facilitates mitochondrial fission. Inhibition of the FAK / Ras / c-myc / ENO1 pathway effectively suppressed aerobic glycolysis and ameliorated hepatic fibrosis.Pkm2 directly interacts with β-linker protein (Ctnnb1) in the cytoplasm of cardiomyocytes (CM), preventing translocation of Ctnnb1 to the nucleus, and subsequently repressing proliferation-related target genes, such as Myc and Cyclin D1). When Pkm2 translocates to the nucleus, it can directly interact with Ctnnb1 in the nucleus of cardiomyocytes to form a complex that cooperates with T-cell factor 4 (TCF4), up-regulates its downstream targets Cy-clin-D1 and C-Myc, and transcriptionally induces genes encoding anti-apoptotic proteins.PKM2 exacerbates proliferation-related genes through activation of the TGF-β / Smad2 / 3 pathway and the Jak2 / Stat3 signaling pathways to exacerbate fibrosis