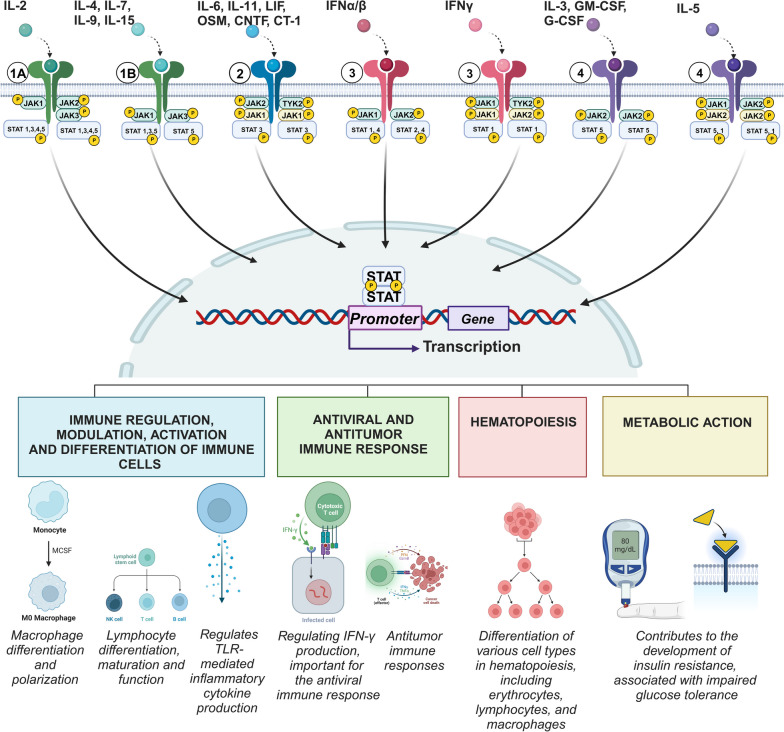
Fig. 1.
Cytokine signaling through the JAK-STAT pathway in physiological conditions. Note: Top: 1A—receptors IL-2 (IL-2Rαβγ); 1B—receptors γc -family cytokines; 2–gp130 subunit receptors; 3—type II cytokine receptors; 4—type I cytokine receptors. Under standard physiological conditions, the JAK-STAT pathway acts as an indispensable cellular communication mechanism. Highlighted are distinct regulatory combinations integral to its functionality, including JAK1-JAK2-JAK3/IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15/JAK1, and JAK3. Center: Central to the depiction is the sophisticated intracellular machinery responsible for transcriptional and translational cascades, which are activated by specific cytokines. Bottom: Four cardinal roles of the JAK-STAT pathway under normal physiological conditions, undisturbed by external stressors, are elucidated: 1) Immune regulation: Modulating, differentiating, and activating immune cells. 2) Defense mechanisms: Spearheading potent antiviral and antitumor responses that determine the body's resistance to the occurrence of infectious and tumor diseases .3) Hematopoiesis: Governing the process of blood cell formation. 4) Metabolic regulation: Navigating cellular energy dynamics. In essence, this figure underscores the JAK-STAT pathway's paramount importance in cellular physiology, particularly in conditions devoid of stress