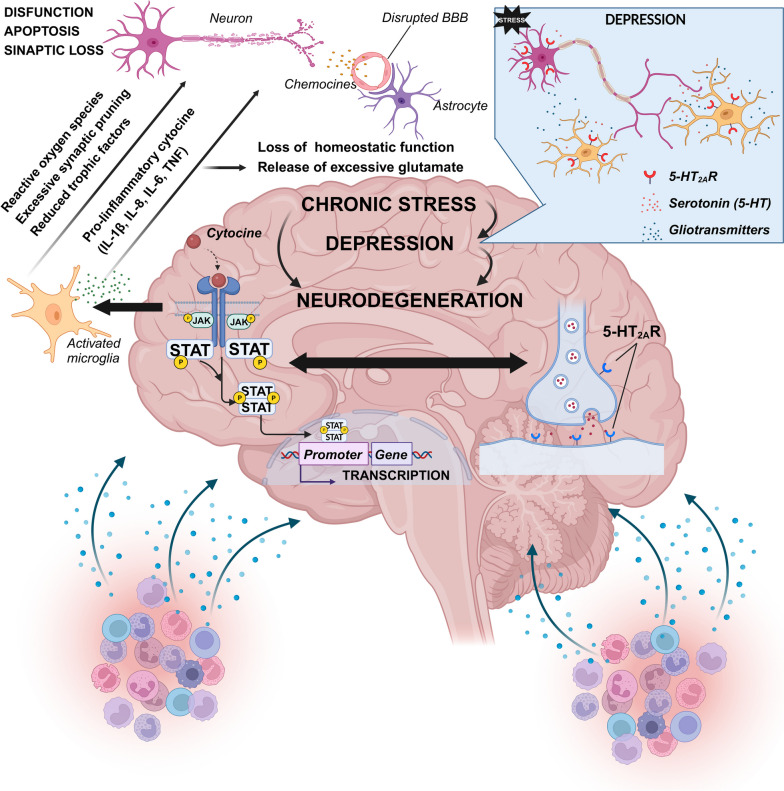
Fig. 2.
JAK-STAT pathway's role in pathological conditions. The figure offers a schematic representation of the JAK-STAT pathway's role in pathological conditions, prominently depicted in the left central portion. It underscores the pathway's association with chronic stress, depression, and neurodegenerative processes. Notably, the 5-HT2A receptor is known to activate several mitogenic pathways, including JAK2-STAT3 and PKC-Ras-Raf-1-MAPK, across various cellular configurations. Concurrently, data illustrate the regulation of STAT3 expression by selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which inhibit the presynaptic serotonin reverse transporter (SERT), suggesting a regulatory feedback nexus between STAT3 and SERT expression. Generally, serotonin is posited to modulate JAK-STAT3 activation in specific cell types, culminating in downstream transcriptional ramifications contingent on serotonin and STAT3. Further, the right central segment of the figure illuminates molecular interactions between STAT3 and pivotal components of the serotonergic machinery. These insights accentuate the JAK-STAT pathway's role in the interface between serotonin receptors and psychiatric afflictions, offering valuable information about prospective therapeutic targets and the underlying mechanisms of these disorders. It is pivotal to highlight that such interactions against a backdrop of stress are accompanied by an elevated concentration of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the peripheral blood, attributed to the activation of immune cells, indicating chronic low-grade systemic inflammation. This interaction is depicted in the bottom left and right sections of the figure. A consequential impairment in the Blood–Brain Barrier (BBB) function leads to microglial activation and the subsequent release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, as presented in the left central segment. This cascade culminates in compromised neuronal functionality