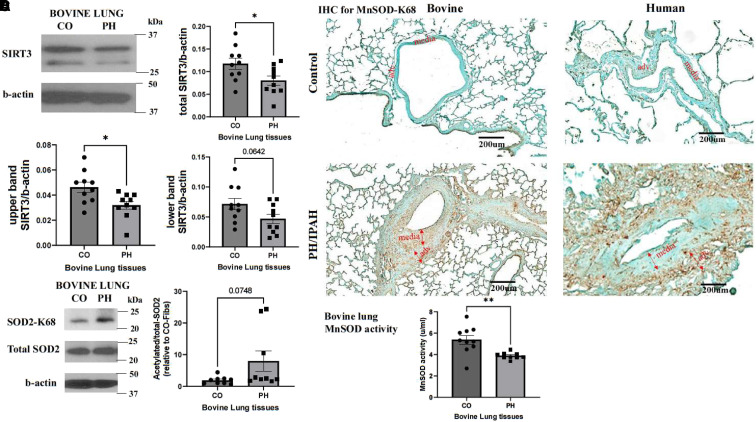
Figure 1.
Lung vasculature in pulmonary hypertension (PH) exhibits decreased SIRT3 (sirtuin 3) protein levels, increased acetylation of mitochondrial SOD2 (superoxide dismutase 2), and decreased MnSOD (mitochondrial SOD) activity. (A) Lung tissues were collected from 2-week hypoxia-induced PH young calves and age-matched normoxic control (CO) animals. Protein lysates were isolated, and western blot was performed with an antibody against SIRT3 (n = 10). Images show a representative blot for SIRT3 and b-actin. The full-length isoform (upper band), short-length isoform (lower band), and total SIRT3 protein levels were analyzed as the ratio to b-actin. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05. (B) IHC staining was performed on lung specimens of hypoxia-induced PH calves, patients with IPAH, and corresponding COs with an antibody that is specific for K68 acetylation of SOD2 (brown color; n = 3 per group; scale bars, 200 μm). (C) Representative western blot images of acetylated MnSOD, total SOD2, and b-actin of bovine PH lungs and CO lungs (n = 9). Data were analyzed as the ratio of acetylated to total SOD2 and are presented as mean ± SEM. (D) MnSOD activity of bovine PH and CO lung tissues was determined using an Invitrogen superoxide dismutase colorimetric assay kit (n = 10). Data are presented as mean ± SEM; **P < 0.01. adv. = pulmonary artery adventitial layer; CO-Fibs = pulmonary artery adventitial fibroblasts from control lungs; IHC = immunohistochemistry; IPAH = idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension; K68 = lysine 68; media = pulmonary artery media layer.