Figure 3.
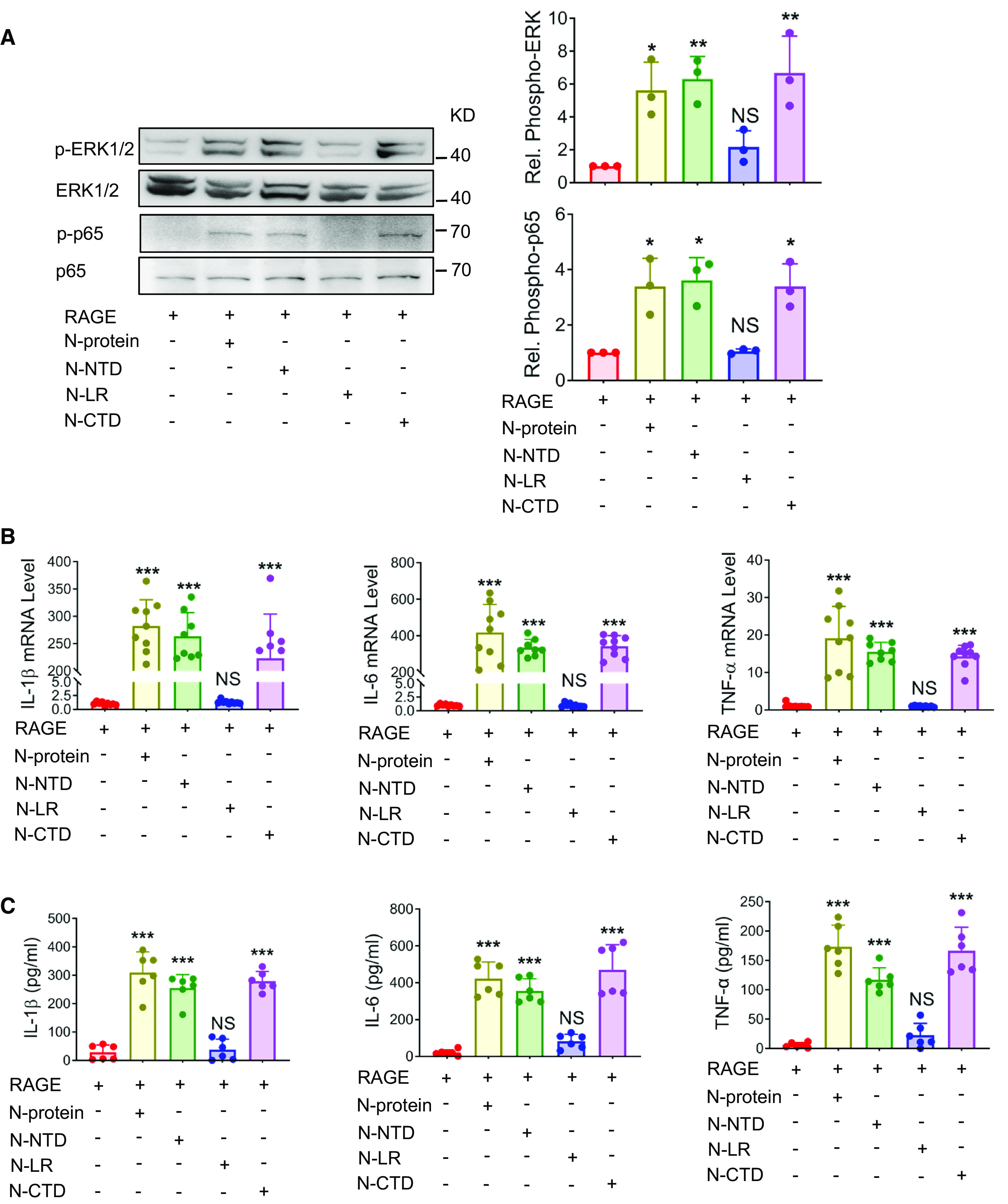
N-NTD and N-CTD induced proinflammatory signaling and immune response. (A) HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with RAGE for 24 hours and treated with recombinant N-proteins expressing full-length, N-NTD, N-CTD, or N-LR (5 μg/ml) for 30 minutes. Cell lysates were analyzed via Western blot using antibodies specific to phosphorylated (upper panels) or total (lower panels) ERK1/2 or NF-ĸB p65. The levels of phosphorylation were quantified with ImageJ software (n = 3). (B and C) HEK293 cells were transiently transfected with RAGE for 24 hours and treated with recombinant proteins expressing full-length, NTD, CTD, or LR of N-protein (5 μg/ml) for 24 hours. (B) The mRNA expression of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in HEK293 cells was quantitated by qRT-PCR (n = 8–9). (C) Culture supernatants were analyzed by ELISA for IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α (n = 6). Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 versus no N-protein treatment. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test (A, B, and C, except TNF-α in B) or Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc test (TNF-α in B) was used for the analysis.
