Figure 6.
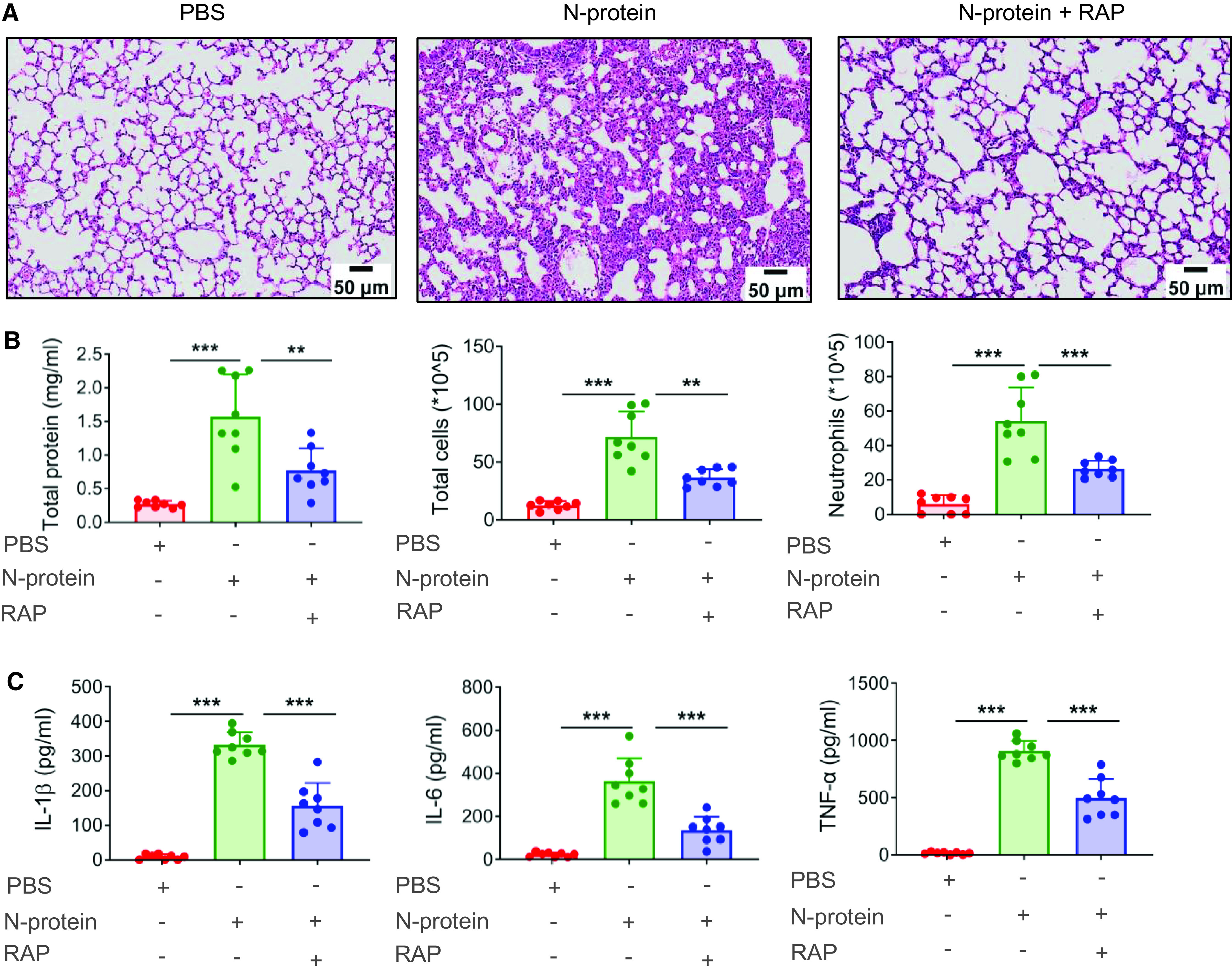
RAGE antagonist reduced N-protein–induced acute lung injury. (A–C) WT C57BL/6 mice were treated with PBS, full-length N-protein (75 μg/mouse), or N-protein + RAGE antagonist RAP (100 μg/mouse, intraperitoneal injection 1 h before N-protein administration). Lung tissue and BAL samples were collected at 24 hours after N-protein insult. (A) Tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (n = 3). Scale bars, 50 μm. (B) Total protein, total cells, and neutrophils in the BAL were determined to evaluate lung injury (n = 8). (C) Levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in the BAL were analyzed via ELISA (n = 8). Data are presented as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test (B and C).
