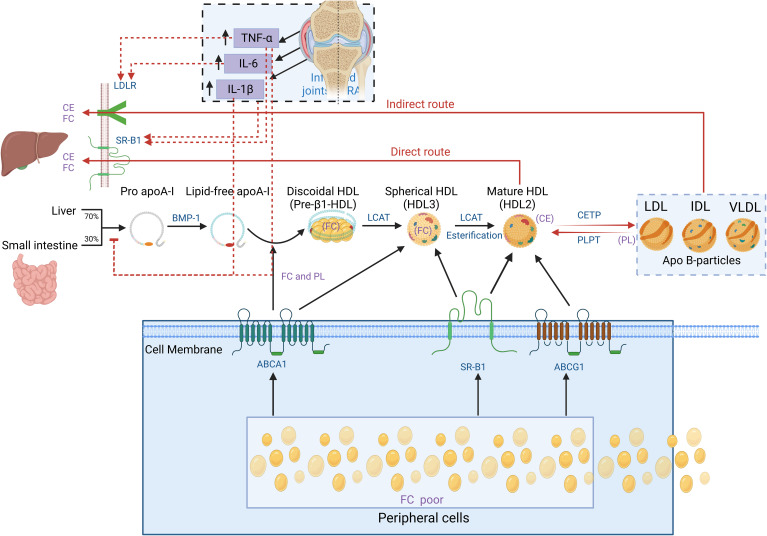
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of cholesterol reverse transportation. Reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) is a process that starts with the formation of pro-Apo A-I in the liver and intestines. Bone Morphogenetic Protein-l (BMP-1) converts it into mature Apo A-I. Free cholesterol (FC) from peripheral cells (including macrophages) flows out to the lipid-free Apo A-I by interacting with ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily A Member l (ABCA1), forming disc-shaped nascent HDL particles. The above process is called cholesterol efflux. Apo A-I on the disc-shaped HDL particle directly interacts with Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) synthesized by the liver to convert the disc-shaped HDL into spheroidal HDL particles. Then, LCAT converts cholesterol into Cholesterol Ester (CE), resulting in cholesterol esterification and HDL maturation. Mature HDL can also obtain additional cholesterol from cells through enzyme ATP-binding cassette transporter G1 (ABCG1) and scavenger receptor B1 (SR-B1). In the direct pathway, the HDL particle docks with SR-B1, which regulates the transfer of cholesterol from HDL particles to cells. In the indirect pathway, the cholesterol transferred by HDL particles is transferred to lipoproteins containing Apo B (e.g., LDL-c and VLDL-c) through cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP). At the same time, phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP) transfers phospholipid (PL) from lipoproteins containing Apo B to HDL. Finally, both the direct and indirect RCT pathways result in the transfer of cholesterol from peripheral sites (mostly macrophages) to the liver and excretion through bile. In the state of RA inflammation, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) produced locally in the joints can enter the circulation. TNF-α and IL-6 can promote LDL metabolism by increasing the expression of LDLR and SR-B1 on the surface of liver cells. TNF-α and IL-1β can inhibit the production of pro-Apo A-I particles in the liver, suppressing HDL generation. As a result, levels of both HDL and LDL in RA decrease.