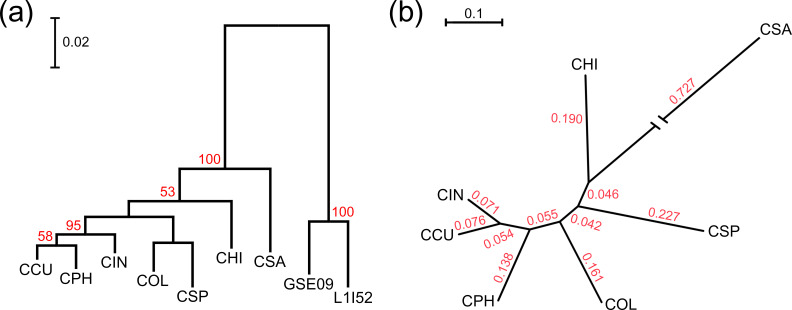
Fig. 2.
Phylogeny of PGP Chryseobacterium species. (a) A phylogenetic tree was reconstructed based on 16S rRNA gene sequences using the maximum-likelihood method, and the robustness of the tree was inferred using a bootstrap procedure with 1000 replicates. Bootstrap probabilities of >50 % are denoted by numbers at branch points. The tree was drawn according to branch lengths scaled according to the evolutionary distance. Flavobacterium anhuiense GSE09 and Flavobacterium sp. L1I52 were used as outgroups. (b) The phylogenomic tree was reconstructed using a concatenated alignment of 1582 orthologous genes. Non-matched regions in the alignments were eliminated and then 1 612 727 nucleotide positions were used to reconstruct the tree. The maximum-likelihood phylogenomic tree was inferred using the RAxML tool with the GTR+gamma model. Evolutionary distances of genes are shown at branch points. Acronyms used for Chryseobacterium species: CCU, C. cucumeris GSE06; CHI, C. hispalense DSM 25574; CIN, C. indologenes PgBE177; COL, C. oleae DSM 25575; CPH, C. phosphatilyticum ISE14; CSA, C. salivictor NBC122; CSP, Chryseobacterium sp. T16E-39; GSE09, F. anhuiense GSE09; and L1I52, Flavobacterium sp. L1I52.