Figure 2.
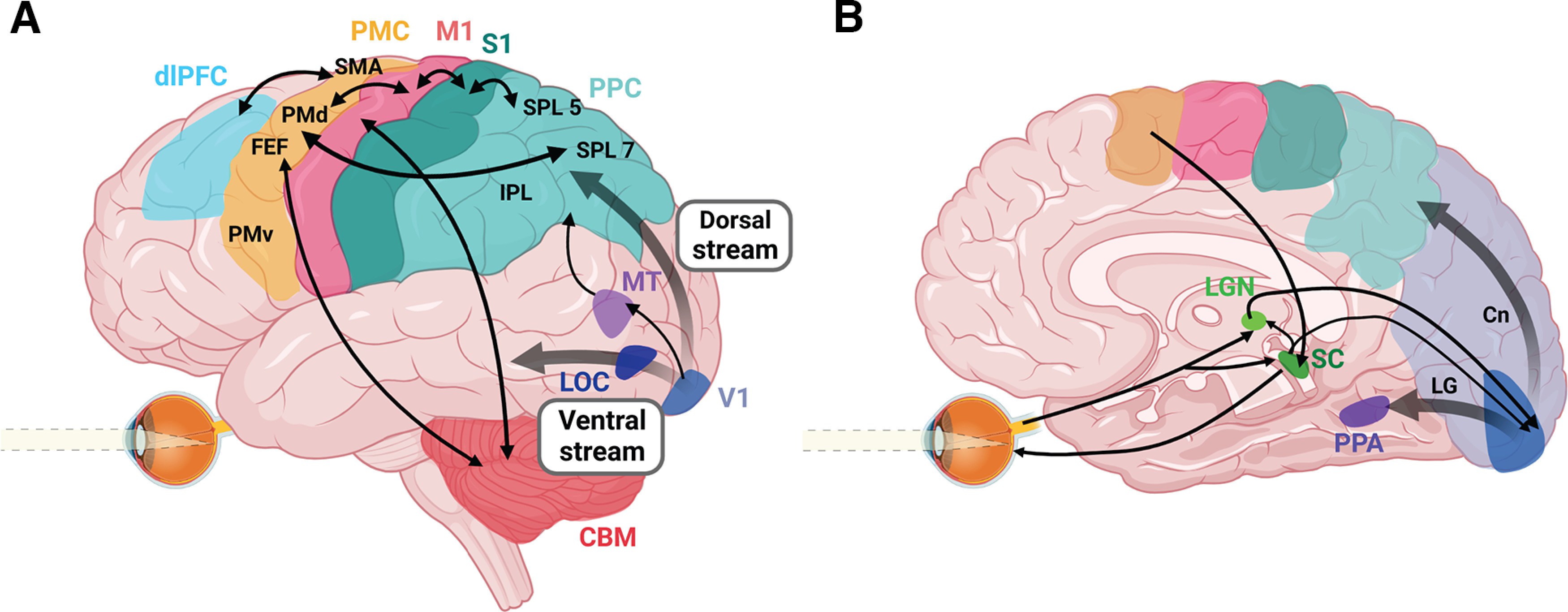
Schematic overview of the major brain regions and pathways involved in goal-directed eye-hand coordination. Pathways for vision, object and motion perception, eye movements, and top-down cognitive strategies are integrated with cortical, subcortical, and cerebellar networks for sensorimotor transformations to produce coordinated action. A, Left brain lateral view. B, Right brain medial view. LOC, Lateral occipital cortex; MT, middle temporal area; PPC, posterior parietal cortex; SPL 7, superior parietal lobule area 7; SPL 5, superior parietal lobule area 5; IPL, inferior parietal lobule; S1, somatosensory cortex; M1, primary motor cortex; PMC, premotor cortex, SMA, supplementary motor area; PMd, dorsal premotor cortex; FEF, frontal eye fields; PMv, ventral premotor cortex; dlPFC, dorsolateral PFC; CBM, cerebellum; SC, superior colliculus; LGN, lateral geniculate nucleus; PPA, parahippocampal place area; LG, lingual gyrus; Cn, cuneus. Created with Biorender.com.
