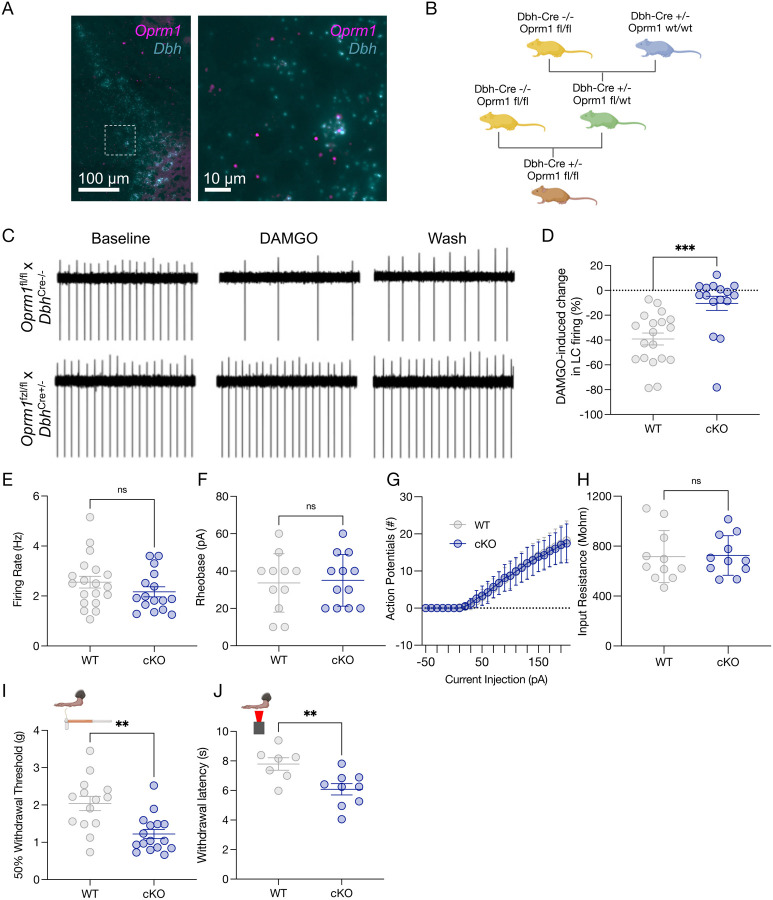
Figure 3. LC-MOR are required for noradrenergic-modulated nociception.
(A) In situ hybridization results of RNA colocalization of oprm1 (purple) and dbh (blue). (B) Cartoon describing Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/− breeding strategy. (C) Cell-attached ex vivo LC recordings in Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre−/− (top) and Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/− (bottom) in response to DAMGO administration. (D) DAMGO-induced cellular inhibition of LC neurons is lost in Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/− mice. Data expressed as mean +/− SEM, n=16–19/group, unpaired parametric t-test ***p<0.001. Excitability parameters of locus coeruleus neurons between WT (Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre−/−) and cKO (Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/−) mice show no significant differences. These measures include (E) baseline firing rate, (F) rheobase, (G) input-output relationship of number of action potentials fired per current step, and (H) input resistance. Data expressed as mean +/− SEM, n=11–19/group, unpaired t-test. (I) von Frey test shows a significant decrease in 50% withdrawal threshold in cKO (Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/−) compared to WT (Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre−/−) control mice. Data expressed as mean +/− SEM, n=14–16/group, unpaired parametric t-test **p<0.01 (L) Baseline thermal withdrawal in Hargreaves testing is also significantly decreased in thermal withdrawal threshold in cKO (Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/−) mice. Data expressed as mean +/− SEM, n=7–8/group, unpaired t-test **p<0.01.