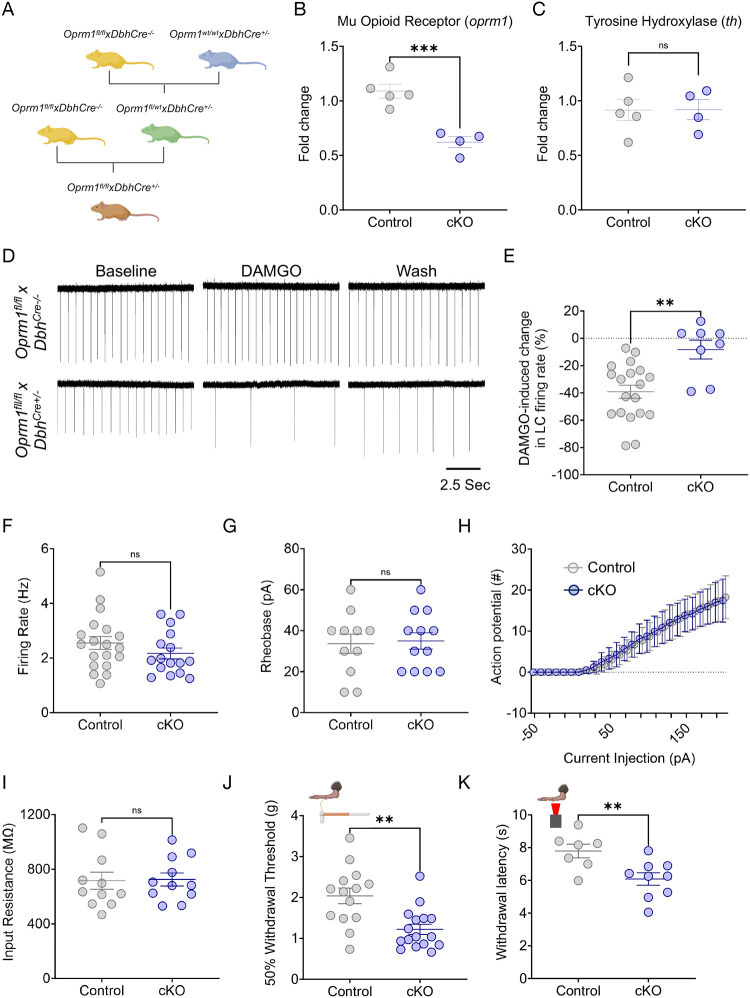
Figure 3. Noradrenergic MOR are required for baseline nociception.
(A) Schematic describing the breeding strategy of Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/− conditional knockout mouse line. (B&C) Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/− mice show lower expression of oprm1, but normal levels of tyrosine hydroxylase (th) mRNA in the LC. Student’s t-test. For oprm1: t = 5.528 ***p<0.001. For th: t = 0.033, ns = not significant. (D) Representative cell-attached ex vivo LC recordings Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre−/− (top) and Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/− (bottom) in response to DAMGO administration. (E) DAMGO-mediated inhibition of LC neurons is lost in Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/− mice. Mann-Whitney test, U =21, **p<0.01. (F-I) Excitability parameters of locus coeruleus neurons between Control (Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre−/−) and cKO (Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/−) mice show no significant differences. These measures include (F) baseline firing rate; Mann-Whitney test, U = 116, ns = not significant, (G) rheobase; Student’s t-test, t = 0.2218, ns = not significant, (H) input-output relationship of number of action potentials fired per current step, and (I) input resistance; Student’s t-test, t = 0.1179, ns = not significant. (J) von Frey test shows a significant decrease in 50% withdrawal threshold in cKO (Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/−) compared to Control (Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre−/−) mice. Mann-Whitney test, U = 37.5, **p<0.01. (K) Baseline thermal withdrawal is also significantly decreased in thermal withdrawal threshold in cKO (Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/−) mice. Student’s t-test, t = 3.009, **p<0.01. Data represented as mean ± SEM.