Figure 5. Restoration of LC-MOR signaling reverses baseline hypersensitivity and receptor rescue reverses neuropathic injury-induced hypersensitivity.
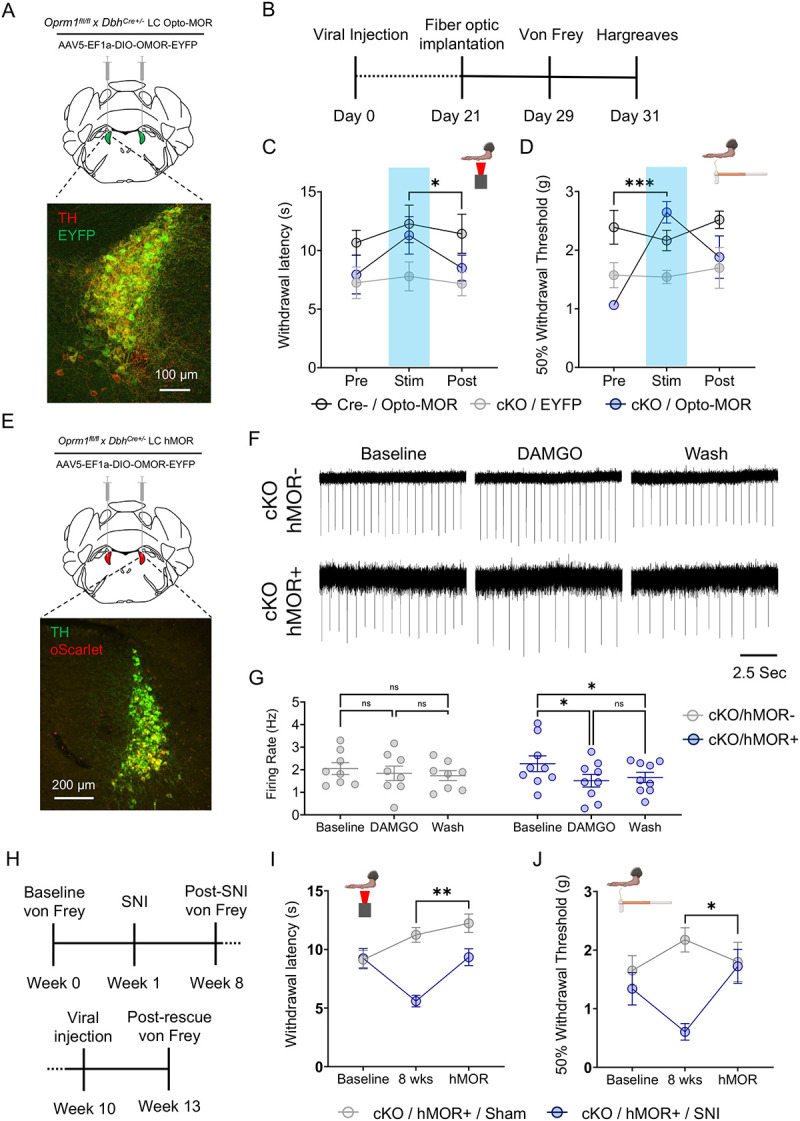
(A) Schematic and fluorescent image for viral strategy expression of opto-MOR in LC. (B) Timeline of opto-MOR behavioral tests. (C) Opto-MOR activation in the LC restores normal thermal sensitivity. Repeated measures two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s posthoc test, F = 3.647 (MOR rescue); 2.764 (Stim. epoch); 0.7294 (interaction); 6.350 (animal), *p<0.05 between cKO:Opto-MOR group Stim vs. Post. (D) Opto-MOR activation significantly reverses baseline mechanical hypersensitivity in von Frey test. Repeated measures two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s posthoc test, F = 3.749 (MOR rescue); 6.370 (Stim. epoch); 5.554 (interaction); 1.724 (animal), ***p<0.001 between cKO:Opto-MOR Pre vs. Stim groups. (E) Schematic and fluorescent image for viral strategy of expression of hMOR in LC. (F) Representative traces of cell-attached recordings in LC neurons with hMOR rescued expression show DAMGO-meditated inhibition of LC neurons is restored in Oprm1fl/flxDbhCre+/− mice (bottom) with hMOR compared to those without (top). (G) hMOR rescue restores DAMGO-mediated inhibition of LC neurons. Repeated measures two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s posthoc test, F = 11.98 (MOR rescue); 0.028 (pharmacology); 3.052 (interaction); 17.47 (cell) **p<0.01. (H) Timeline of behavioral measurements following neuropathic injury and rescue of hMOR in the LC. (I) hMOR expression reverses neuropathic injury-induced thermal hypersensitivity. Repeated measures two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s posthoc test, F = 4.805 (SNI surgery); 34.77 (SNI development & MOR rescue); 6.847 (interaction); 0.558 (animal), **p<0.01. (J) hMOR expression reverses neuropathic injury-induced mechanical hypersensitivity. Repeated measures two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s posthoc test, F = 1.034 (SNI surgery); 10.81 (SNI development & MOR rescue); 4.560 (interaction); 0.833 (animal), *p<0.05. Data represented as mean ± SEM.
