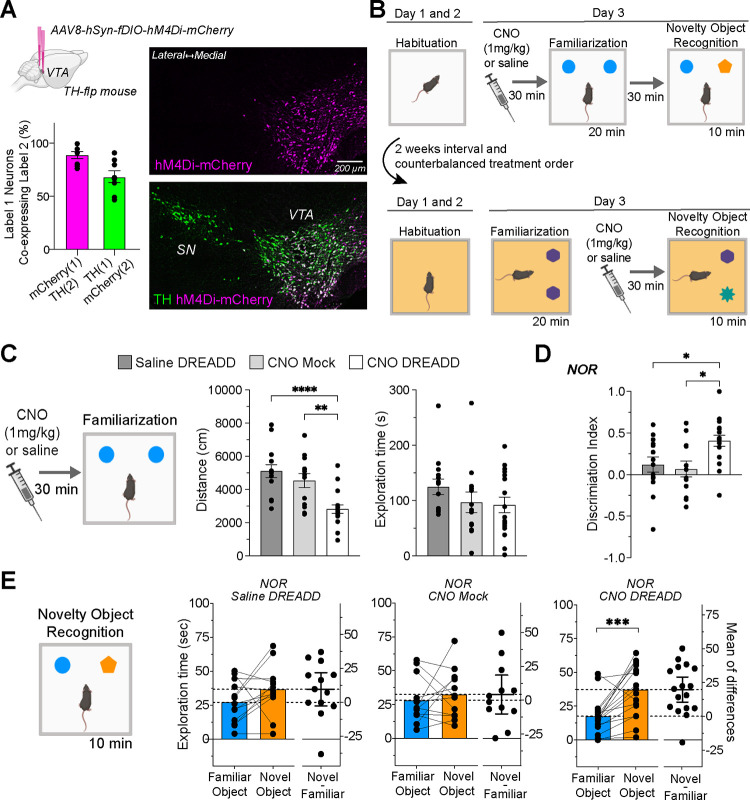
Figure 3. Effects of Chemogenetic Inhibition during Familiarization on Novel Object Recognition.
(a) Brain diagram describing bilateral VTA DREADD virus injections. The graph below details the virus’s specificity (magenta bar: percentage of mCherry+ neurons co-expressing TH+) and its efficacy (green bar: percentage of TH+ neurons co-expressing mCherry+). Accompanying photomicrographs display DREADD virus (hM4Di-mCherry) expression in VTA TH+ neurons. (b) NOR paradigms schematic detailing CNO injection timing, either before or after the familiarization session, using a within-subject counterbalanced design. (c) Pre-familiarization CNO injections reduce travel distance (****P < 0.0001; **P = 0.032) without affecting object exploration time. (d) Discrimination index for object exploration during NOR. CNO DREADD group (n=17) showed increased discrimination compared to Saline DREADD (n=13, *P = 0.046) and CNO mock groups (n=12, *P = 0.018). (e) NOR session exploration times, with the CNO DREADD group displaying a pronounced novel object preference (*P = 0.0004).