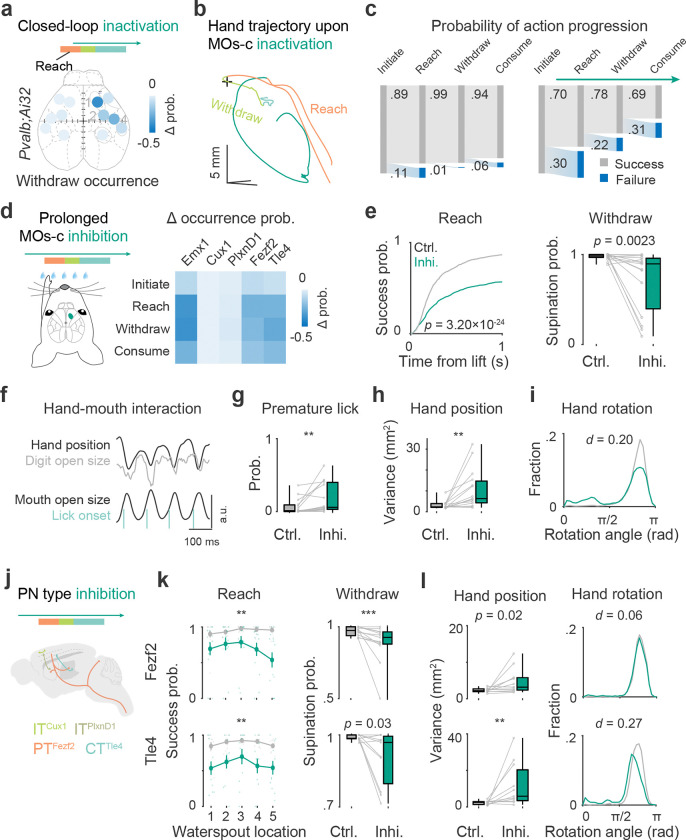
Fig 3. MOs-c PT and CT are required for the progression and coordination of RWD.
a. Photoinhibition mapping of cortical areas by closed-loop activation of inhibitory interneurons. Inactivation of the contralateral areas of MOs-c (1), MOp-ul (2), and SSp-ul (4) decreased supination probability. Color scale represents changes in success probability between inhibition and control trials. ( Pvalb;Ai32 mice, see Supplementary Table 1 for statistics)
b. Perturbation of movement progression upon close-loop MOs-c inactivation during reach in an example control and inhibition movement trajectory. In the inhibition trial, the reach was aborted; the hand returned to the start position, followed by another failed attempt.
c. Impaired action sequence progression in control (left) and inhibition (right) trials upon contralateral MOs-c inhibition. 18% (81/441) control trials and 63% (209/331) inhibition trials failed to complete the RWD sequence. ( Pvalb;Ai32 mice)
d. Effects of prolonged inhibition of PN types by expressing optogenetic inhibitory opsins in MOs-c (turquoise). Heatmap summarized the change in success probability of action phases upon prolonged inhibition of each PN type compared with control trials. Same mice for all following panels. ( sessions from 8 PNEmx1 mice; 8 sessions from 6 ITCux1 mice; 12 sessions from 7 ITPlxnD1 mice; 13 sessions from 7 PTFezf2 mice; 11 sessions from 6 CTTle4 mice.)
e. Reduction of reach and withdraw success probability with prolonged PNEmx1 inhibition. Reach was quantified as target contact probability from all trials with successful lifts (two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test, KS distance ). Withdraw was quantified as supination probability with successful reach (Wilcoxon rank sum test, ).
f. Coherent hand-mouth movement time series during drinking. Hand upward position, digit open size, mouth open area, and lick onset variables are indicated.
g. Increased premature lick probability during PNEmx1 inhibition (, Wilcoxon rank sum test, ).
h. Increased variance in hand position relative to the mouth upon the onset of hand lick during PNEmx1 inhibition (, Wilcoxon rank sum test, ).
i. Abnormal hand posture during drinking with prolonged PNEmx1 inhibition indicated by palm-facing direction at lick onset ( control and 9186 inhibition licks, two-sample KS test, ).
j. Schematic of the prolonged inhibition of MOs-c PN types.
k. PT Fezf2 and CTTle4 inhibition on success probability of reach and withdraw. Left: ANOVA; PTFezf2 inhibition inhibition . Note the target location-dependent impairment in PTFezf2 (inhibition × target ) but not in CTTle4 (inhibition × target ). Right: Wilcoxon rank sum test, .
l. Variance in hand position (left) and hand posture (right) during PT Fezf2 and CTTle4 inhibition. (Left: Wilcoxon rank sum test, . Right: two-sample KS test, .)