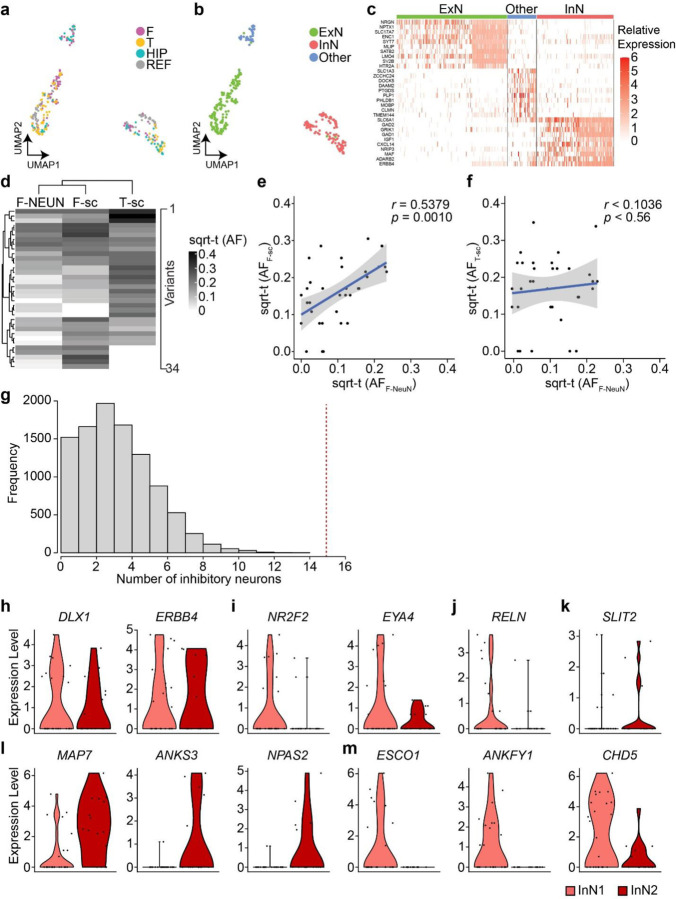
Extended Data Fig. 8. Quality controls of the ResolveOME dataset in ID05.
(a) A UMAP plot of snRNA-seq using 225 NEUN + nuclei and 121 aggregated reference cell types52,53. F, frontal; T, temporal; HIP, hippocampus; REF, reference dataset. (b) UMAP labeled by cell types. Note that UMAP clusters separate by cell type (ExN, InN or Other) more than by location. (c) Relative expression of cell type markers within clusters, confirming cell identity. (d) Hierarchical clustering based on sqrt-t AFs of 34 informative MVs shared in 5 to 29 cells in single-nuclear data. F- NEUN, sorted frontal NEUN+ nuclei pool; F-sc, pseudo-bulk snMPAS data from a frontal lobe punch; T-sc, snMPAS data from a frontal (F) lobe punch. (e) Correlation between sqrt-t AFs of MVs between F- NEUN and F-sc. (f) Correlation between sqrt-t AFs of MVs between F- NEUN and T-sc. Linear regression with upper and lower 95% prediction intervals displayed by blue solid lines and gray surrounding area; sqrt-t (AF), sqrt-t AF. Pearson’s Product-Moment correlation in e and f. (g) Null distribution of the frequency of the number of inhibitory neurons carrying MVs exclusively detected in one lobe and shared with at least two other local cells, including one excitatory neuron within the same lobe. 10,000 permutations. Portion to the right of the red dashed line, compared to the entire distribution, represents the probability (p < 0.0001, one-tailed permutation test) of having 15 or more InNs. (h–m) RNA expression levels of informative genes between InN1 (n = 17) and InN2 (n = 16) (Fig 4b) in snRNA-seq. (h) Comparable expression levels of inhibitory neuronal markers between both groups. (i) Decreased tendency for the expression of CGE-derived cell markers in InN2 compared to InN1, implying COUPTFII+ inhibitory neurons are unlikely InN1, consistent with previous observations in sorted nuclear populations. (j) RELN+ inhibitory neuronal marker showed decreased expression tendency in InN2 compared to InN1. (k) Increased expression tendency for parvalbumin-positive (PV+) inhibitory neuronal marker in InN2 compared to InN1, implying dorsally derived inhibitory neurons include PV+ neurons. (l, m) top 3 genes increased (l) or decreased (m) in InN2 compared to InN1 among the most variable 3000 protein-coding genes.