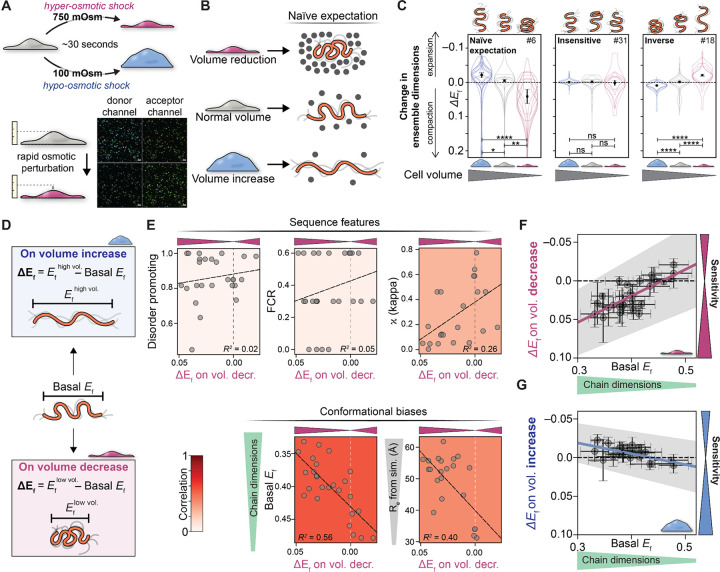
Figure 4. IDR ensemble dimensions explain responsiveness to changes in cell volume.
(A) Using rapid osmotic perturbation, cellular volume is reduced (top) or expanded (bottom), altering intracellular crowding within seconds. These timescales ensure changes in FRET efficiency (ΔEf) reflect physical changes in the cellular environment, as opposed to the downstream consequences of a response pathway driven by phosphorylation or gene expression. (B) If macromolecular crowding were the only determinant of IDR dimensions, we would naively expect a decrease in cell volume to drive ensemble compaction (top) and an increase in cell volume to drive ensemble expansion (bottom). (C) Actual data for sequences 5/31/18, demonstrating that while some sequences respond as expected by the naive model (left), others show complete insensitivity (middle) while others show inverse behavior, expanding upon volume reduction (right). These results illustrate the complex range of sequence-dependent responses available to IDRs. N for each violin plot is in Table S5. (D) To quantitatively compare different sequences, we can compare basal FRET efficiency (Ef under normal conditions) with the change in FRET efficiency ΔEf upon increase or decrease in cellular volume. (E) Sequence properties (fraction of disorder-promoting residues, FCR, and kappa) are weakly correlated with molecular function (see also Fig. S10), here defined as the change in FRET efficiency upon cell volume decrease. In correlating ΔEf vs. many sequence parameters, Ef basal (and, to a lesser extent, ensemble dimensions from coarse-grained simulations) offer the strongest predictive power of molecular function (Fig. S10). (F) Plotting ΔEf upon the increase in cellular volume and (G) ΔEf upon the decrease in cellular volume reveals that the most sensitive sequences (those with the largest change in Ef) are strongly correlated with those that start out being more expanded under basal conditions.