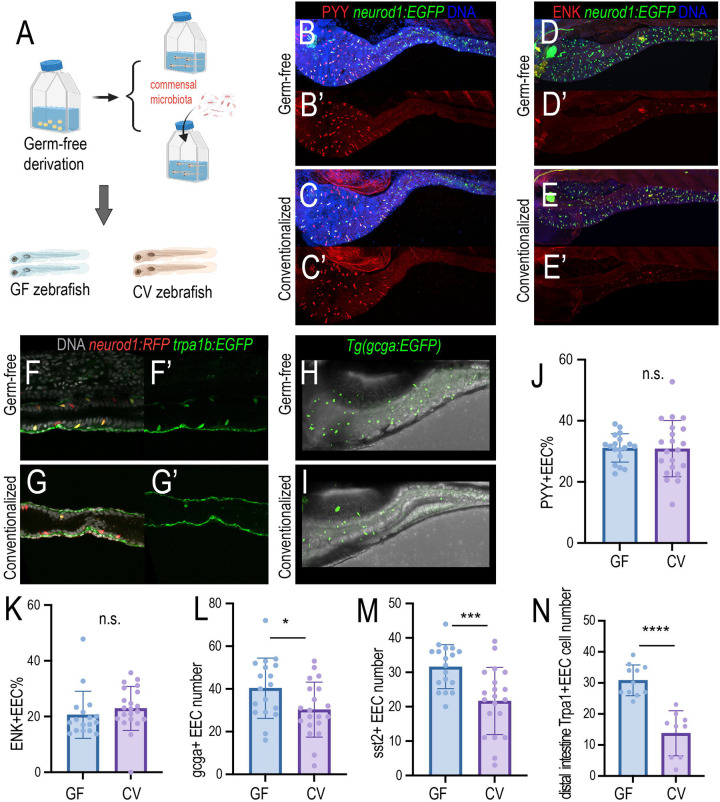
Figure 1. Gut microbiota modulates the EEC subtype.
(A) Gnotobiotic zebrafish experimental procedure to examine the effects of gut microbiota on EEC subtype formation. Commensal microbiota was colonized at 3pdf and the zebrafish were fixed at 7dpf for immunofluorescence staining. (B-C’) Confocal projection of the representative germ-free (GF) and conventionalized (CV) zebrafish intestine. The total EECs were labeled by the Tg(neurod1:EGFP) transgene (green), and the PYY+EECs were labeled via the PYY antibody. (D-E’) Confocal projection of the representative germ-free (GF) and conventionalized (CV) zebrafish intestine showing the ENK+ EECs. (F-G’) Confocal projection of the representative germ-free (GF) and conventionalized (CV) zebrafish intestine showing the Trpa1+ EECs in the distal intestine. (H-I) Confocal projection of the representative germ-free (GF) and conventionalized (CV) zebrafish intestine showing the gcga+ EECs. (J-N) Quantification of the PYY+EECs, ENK+EECs, gcga+EECs, sst2+EECs and the Trpa1+EECs in GF and CV zebrafish. Student t-tests were used for statistical analysis. Each dot represents individual zebrafish. *p<0.05, *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001.