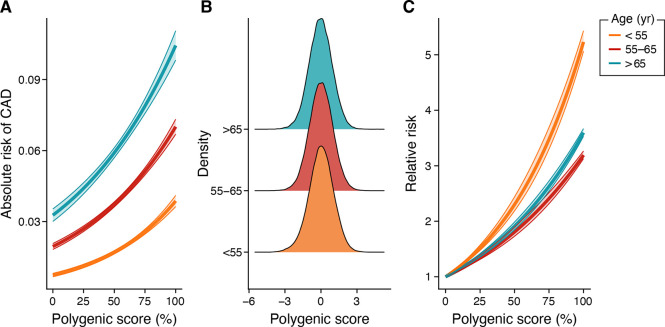
Figure 2. Absolute and Relative Incidence Rate of CAD by Genomic Risk per Age Group.
In the UK Biobank (N=327,837), three age groups (<55, 55–65, and >65 years) at risk estimation were used to compare the stratification of the observed absolute and relative risk across polygenic score percentile. (A) The absolute risk of CAD increased with increasing polygenic score percentile in all three age groups, and older participants had higher absolute risk of CAD. Absolute risk of CAD ranged from 0.7 to 3.9% in the <55 years age group, 1.9 % to 7.0 % in the 55–65 years age group, and 3.3 to 10.4% in the >65 years age group. (B) The polygenic score distribution was similar across three age groups. (C) Relative risk gradient of genomic risk is greatest for younger age groups. The 99th percentile of polygenic score was associated with a 5.2-fold increase in risk in the <55 years age group, 3.6-fold increased risk in the 55–65 years age group, and 3.2-fold increase in risk in the >65 years age group.
CAD: coronary artery disease. PRS: Polygenic risk score.