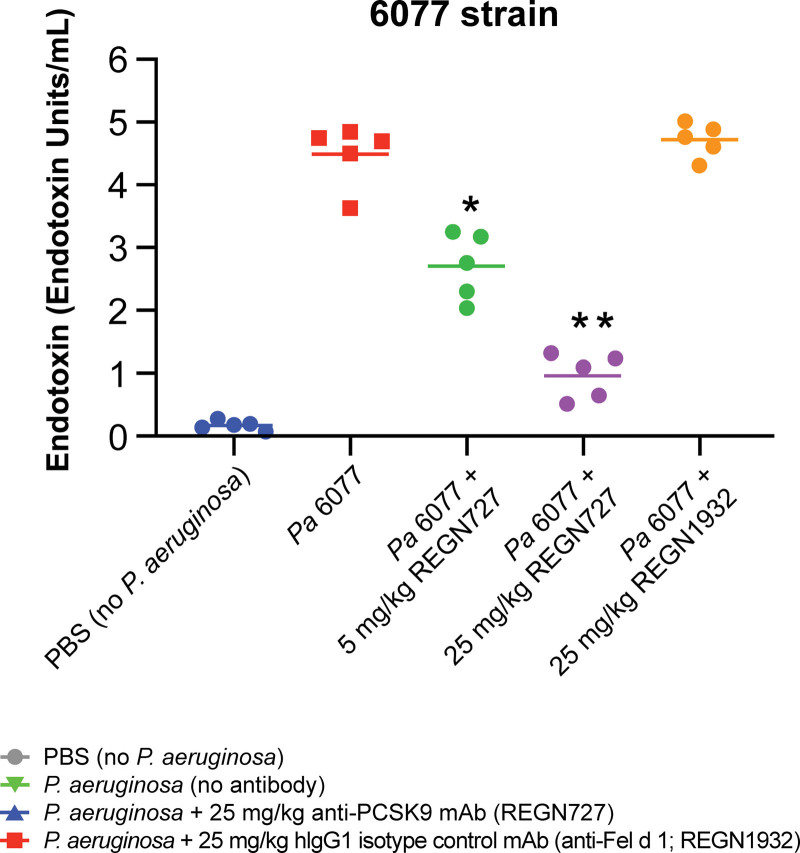
Figure 3.
Effects of anti-proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) monoclonal antibody (mAb) on lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels and survival in a live bacteria-induced sepsis model due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. C57Bl/6J mice were given a single subcutaneous injection of the indicated doses of human immunoglobulin G1 (hIgG1) Regeneron (REGN) monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) 48 hr before intraperitoneal injection of live P. aeruginosa (Pa) strains PAK (at 1.5 × 107–2.5 × 107 colony-forming units [CFUs]/mouse; n = 60), PA14 (at 5 × 107–7 × 107 CFU/mouse; n = 30), or 6077 (at 2.5 × 106–7 × 106 CFU/mouse; n = 40), in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). LPS was measured in serum 16 hr after infection in mice (n = 5 per group), and survival was monitored for up to 96 hr. LPS was lower at 16 hr among mice receiving anti-PCSK9 mAb in strain 6077. *p < 0.001 by unpaired t test; **p < 0.0001 by unpaired t test. mAb to cat allergen, Fel d 1 is used as a control in this experiment, PA14 = P. aeruginosa strain 14, PAK = P. aeruginosa strain K.