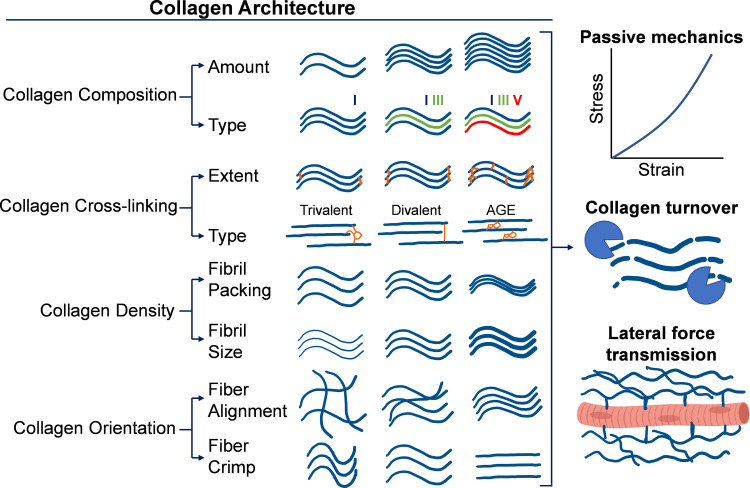
Figure 1.
Schematic of collagen architectural features within the skeletal muscle extracellular matrix (ECM). The muscle ECM contains a significant amount of fibrillar collagen, which has a complex architecture that dictates many functional properties of muscle. Composition of collagens relates to their total content and distribution among types of collagens. Cross linking relates to the degree of collagen cross links, both enzymatic and nonenzymatic, that exist between collagen molecules and fibrils. Density relates to how tightly collagen fibrils and fibers are packed together within the matrix. Orientation of collagen fibers and fibrils relates to their directional alignment and their crimp. These properties of collagen architecture relate to passive mechanics, collagen turnover, and lateral force transmission. AGE, advanced glycation end product. Figure made using BioRender.com.