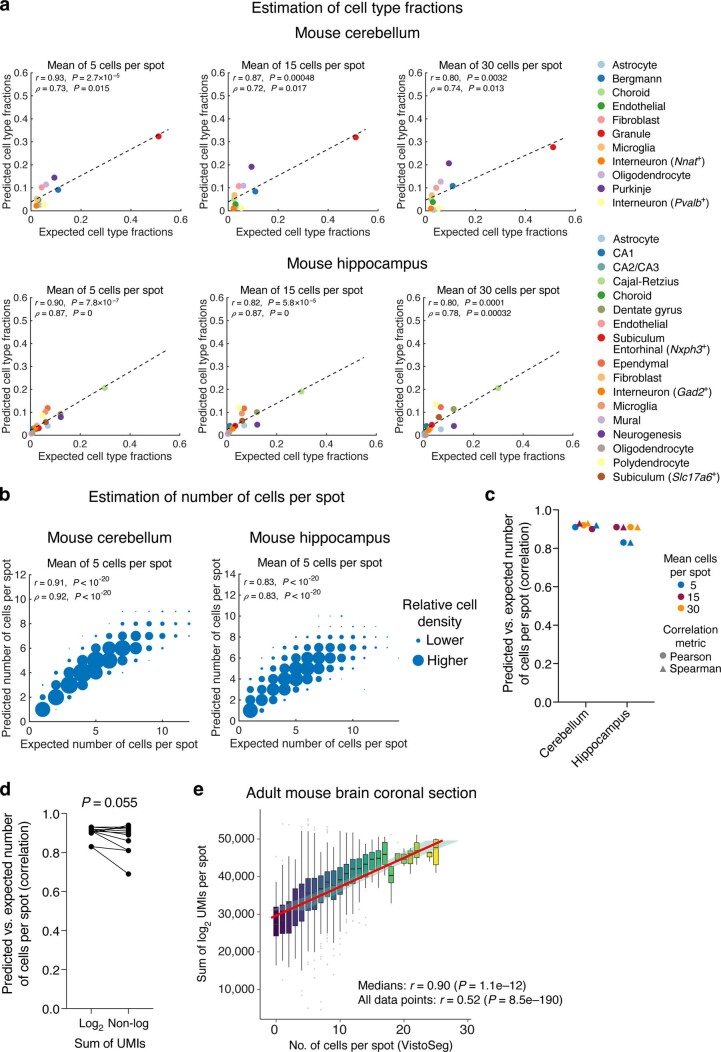
Extended Data Fig. 3. Estimation of cell type fractions and the number of cells per spot in bulk ST data.
a, Application of Spatial Seurat to infer cell type fractions in simulated ST datasets (Methods). Scatter plots show ground truth cell type fractions (x-axis) versus estimated fractions (y-axis) for simulated ST data of mouse cerebellum (top) and hippocampus (bottom) sections with different spot resolutions. Single-cell RNA sequencing data were first perturbed with the addition of noise to 5% of the transcriptome, as described in Methods. b, Scatter plot showing the number of cells per spot estimated by CytoSPACE in simulated ST datasets (y-axis; Methods) versus ground truth (x-axis) at a mean of 5 cells per spot for mouse cerebellum and hippocampus sections. Relative density is depicted by point size. Concordance and significance were assessed by Pearson r or Spearman ρ and a two-sided t test, respectively. c, Same as b but showing correlation coefficients (Pearson and Spearman) for all analyzed spot resolutions. All correlations are significant (P < 10–20). d, Paired analysis showing the difference in performance between log2 adjustment and the non-log linear scale for predicting the number of cells per spot for all six combinations of spot resolutions in simulated ST datasets (mean of 5, 15, and 30) for Pearson and Spearman correlation coefficients. Statistical significance was calculated with a two-sided paired Wilcoxon test. e, Concordance between the number of cells per spot imputed by the default RNA-based approach implemented in CytoSPACE (y-axis) and a cell segmentation algorithm (VistoSeg) respectively applied to paired gene expression data and a histological image of an adult mouse brain coronal sample profiled by 10x Visium. The box center lines, box bounds, and whiskers indicate the medians, first and third quartiles and minimum and maximum values within 1.5× the interquartile range of the box limits, respectively. Linear regression, shown with a 95% confidence interval, was applied to the box plot medians. In panels a and b, concordance was assessed by Pearson correlation (r), Spearman correlation (ρ), and/or linear regression (dashed lines). A two-sided t-test was used to assess whether each correlation result was significantly nonzero. No adjustments for multiple comparisons were made.