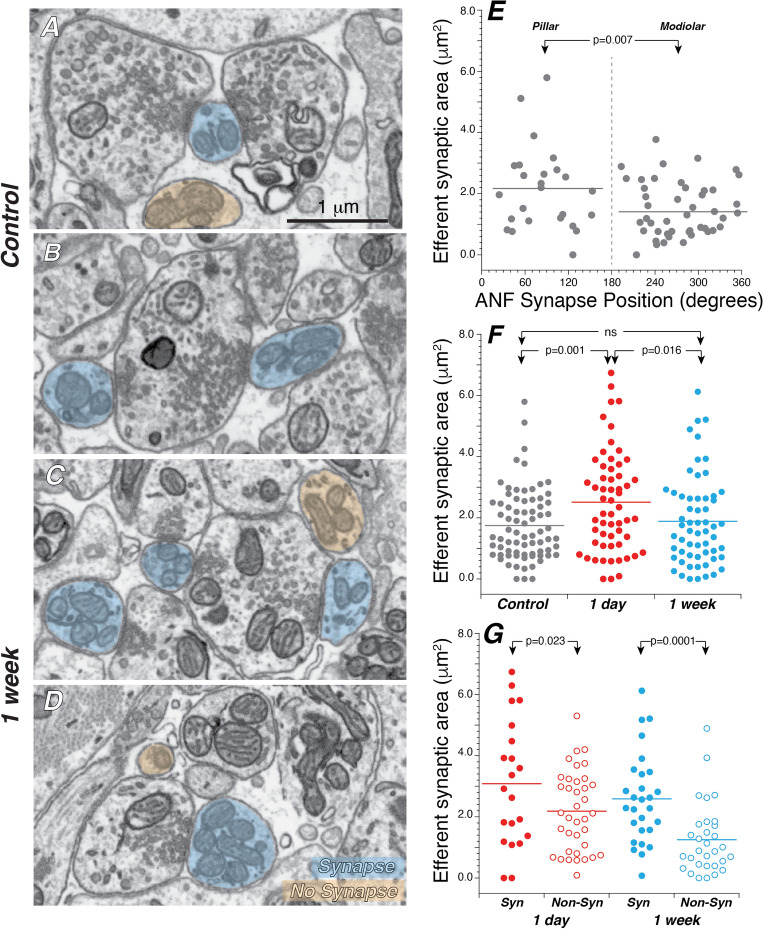
Figure 9.
Efferent innervation is richer on pillar side ANFs and increases transiently after noise, especially in fibers that maintain synaptic contact with the IHCs. (A–D) FIB-SEM images from control (A,B) and exposed (C,D) ears in which some of the ANFs are highlighted in blue or orange depending on whether the contact they make with an efferent terminal is considered synaptic (blue) or not (orange). (E) In the control ears, modiolar-side ANFs receive less efferent innervation than pillar-side ANFs. (F) After exposure, the surface area of efferent synaptic contacts increases at 1 day then returns to control values at 1 week. (G) In exposed ears, at both 1 day and 1 week post exposure, non-synapsing ANFs have significantly less efferent innervation than ANFs that retain their synaptic connections. P values for comparisons across survival times are not indicated in (G). In all panels horizontal lines on dot plots indicate the mean of each distribution. Data are from all the same fibers shown in Figs. 7 and 8.