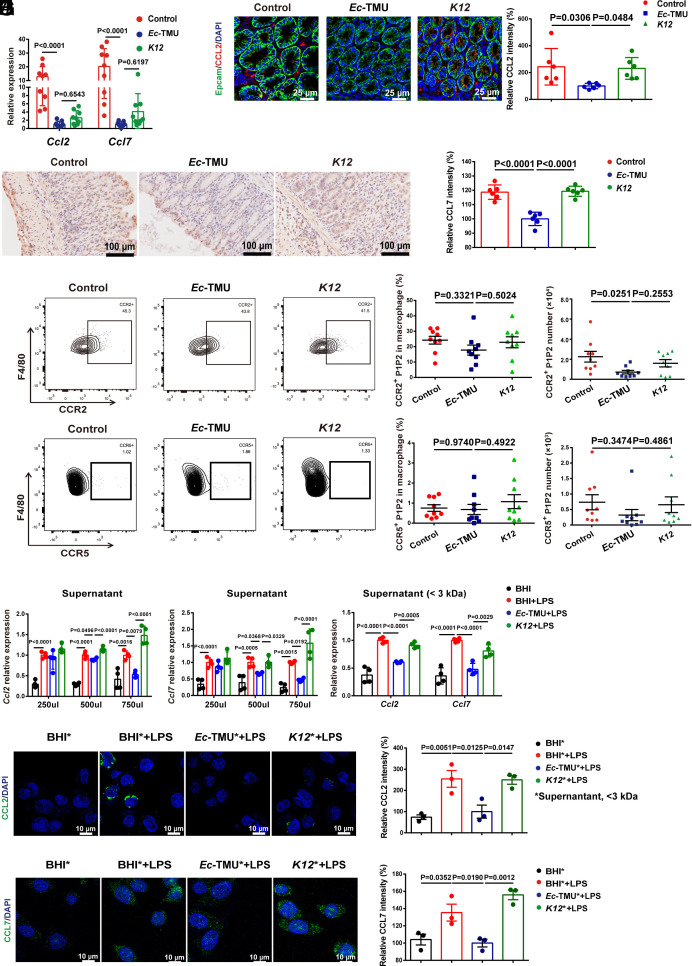
Fig. 4.
Ec-TMU supernatant reduces CCL2/7 expression in epithelial cells. On day 7, mice were killed in the model of Fig. 2A. (A) mRNA expression levels of Ccl2 and Ccl7 in the colons. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of CCL2 expression in mouse colons. (Scale bar: 25 μm.) Blue, nucleus; green, Epcam; red, CCL2. (C) Immunohistochemical analysis of CCL7 expression in mouse colons. (Scale bar: 100 μm.) Lymphocytes in cLP of mice from the Ec-TMU, K12, or control groups were analyzed. (D) The percentage and number of CCR2+ macrophages in cLP. (E) The percentage and number of CCR5+ macrophages in cLP. (F and G) SW480 cells were stimulated with bacteria culture supernatant and LPS (10 μg/mL) for 3 h. mRNA levels of Ccl2 (F) and Ccl7 (G) were evaluated for cells incubated with BHI broth, Ec-TMU, and K12 culture supernatant. (H–J) SW480 cells were simultaneously stimulated with bacteria culture supernatant (750 μL, <3 kDa) and LPS (10 μg/mL) for 3 h. (H) mRNA levels of Ccl2 and Ccl7 were evaluated for cells incubated with BHI, BHI+LPS, Ec-TMU culture supernatant (<3 kDa) + LPS, or K12 culture supernatant (<3 kDa) + LPS. (I and J) Immunofluorescence analysis of CCL2 (I) and CCL7 (J) in cells. Asterisks indicate <3-kDa fractions of bacterial supernatant. CCL2 and CCL7: green; DAPI: blue. (Scale bar: 10 μm.) n = 9 (A, D, and E), n = 6 (B and C), n = 4 (F–H) and n = 3 (I and J) in each group. Data are the mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA.