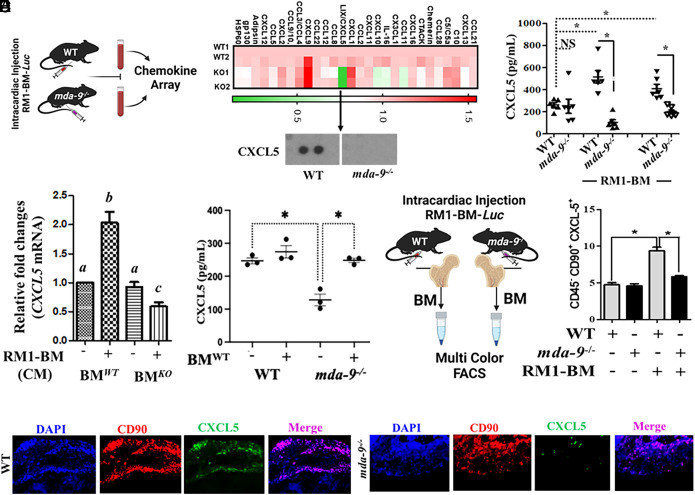
Fig. 3.
CXCL5 expression correlates positively with bone metastasis progression. (A) Serum samples were isolated from tumor-bearing mice [14 d after intracardiac (I.C.) injection, 3 × 104 cells/mouse], and protein-based arrays were analyzed as described by R&D Biosystems. Heatmap is presented. Cropped blot for CXCL5 is presented in the bottom panel. (B) CXCL5 level in serum from mice under different experimental conditions (sham/basal level vs. 14-d post-I.C. or postorthotopic implantation (1 × 104 cells/mouse). A mouse-specific CXCL5 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (R&D Biosystems) was used for determining CXCL5 levels. (C) Bone marrow (BM) cells were isolated from WT (BMWT) and mda-9−/− (BMKO) mice and stimulated with tumor cell–derived conditioned media for 12 h. Total cellular RNA was extracted, and qPCR was performed to detect mouse CXCL5 mRNA. Data are presented as fold-change relative to the unstimulated wild-type (BMWT) group. Different letters in two variables are statistically significant (P < 0.05). (D) CXCL5 levels in serum from tumor-bearing mice receiving “sham” (represented as “−“) or “WT” (represented as “+”) bone marrow (experiments described in Fig. 1E). *P < 0.01. (E) A total of 3 × 104 RM1-BM-Luc cells were injected by the intracardiac (I.C.) route into WT and mda-9−/− mice (schematically presented in the left panel). Fourteen days postinjection, total BM cells were isolated and stained for lineage-specific cell surface markers and intracellular CXCL5 expression to identify the specific cell population(s) that differentially respond to tumor cells. Percentages of CXCL5 expression in bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stromal cells: (CD45−CD90+) are presented. *P < 0.05. (F) Tumor-implanted bones (from animals in Fig. 2A) were immunostained with different antibodies as indicated, and representative photographs are presented.