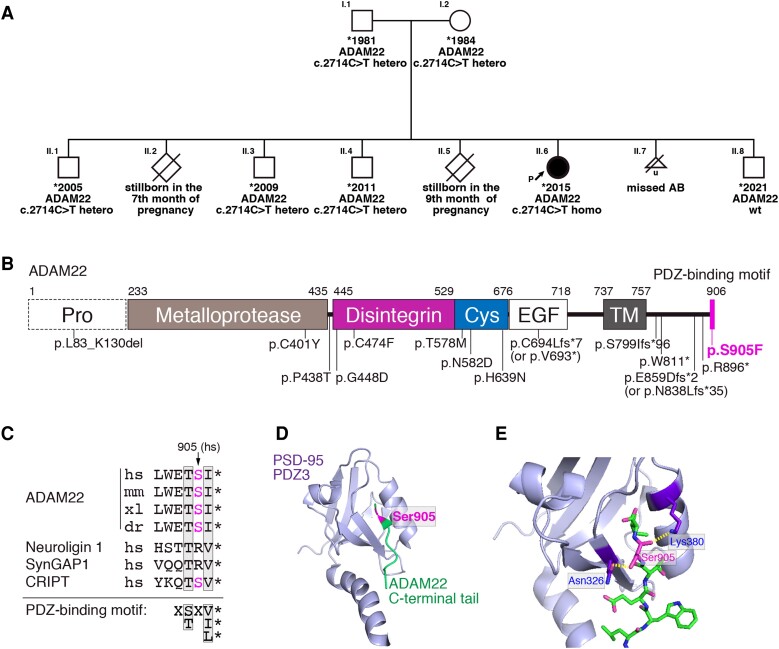
Figure 1.
Genetic study and structural correlates of the ADAM22 c.2714C > T variant. (A) Pedigree of the family and segregation analysis of the ADAM22 c.2714C > T variant. (B) Domain organization of ADAM22 and location of all reported pathogenic ADAM22 variants. The p.S905F variant is located in the PDZ-binding motif at the C-terminus (magenta stick). Pro, prodomain; Cys, cysteine-rich domain; EGF, EGF-like domain; TM, transmembrane domain. Note that the ADAM22 has no metalloprotease activity. (C) Cross-species sequence alignment of the PDZ-binding motif of ADAM22. hs, Homo sapiens; mm, Mus musculus; xl, Xenopus laevis; dr, Danio rerio. The PDZ-biding motifs of neuroligin 1, SynGAP1 and CRIPT that bind to the 3rd PDZ domain of PSD-95 (PDZ3) are aligned. (D and E) Structure of the complex of the ADAM22 PDZ-binding motif (green) and PSD-95-PDZ3 (purple) (D). Close-up view of the interface between the ADAM22 C-terminal tail and PSD-95-PDZ3 (E). The magenta indicates the position of the Ser905 residue. The yellow dotted lines represent hydrogen bonds between ADAM22 Ser905 residue and PSD-95-PDZ3 domain. PDB accession code, 7CQF.