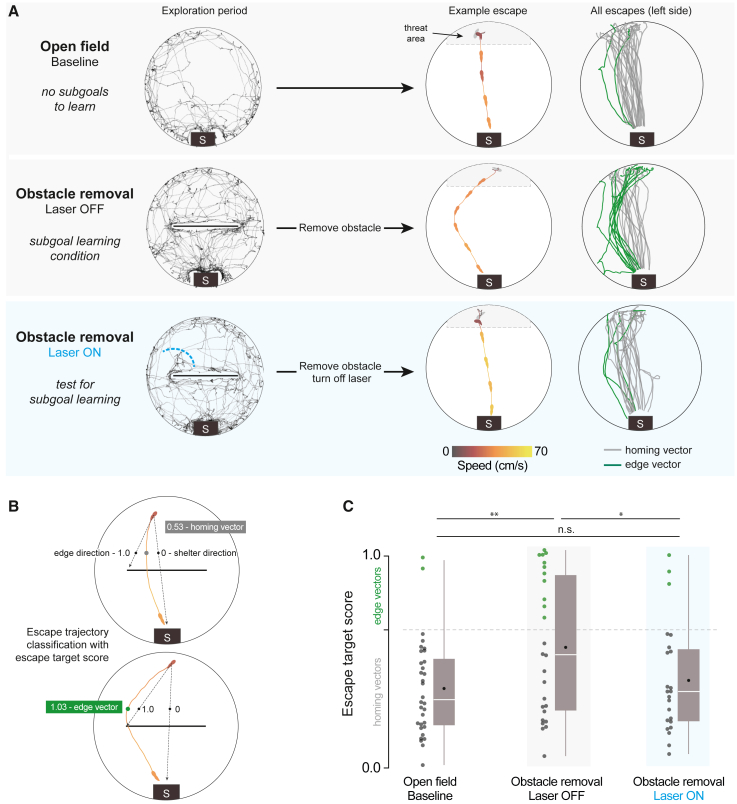
Figure 2.
Interrupting spontaneous edge-vector runs abolishes subgoal learning
(A) Black traces show exploration during an example session (open field: 10 min, obstacle removal: 20 min). Lines and silhouette traces show escape routes from threat onset to shelter arrival; open field: 29 escapes; obstacle removal (laser off): 26 escapes; obstacle removal (laser on): 23 escapes. All: n = 8 mice.
(B) The initial escape target is the vector from escape initiation to 10 cm in front of the obstacle (black dots), normalized between 0 (shelter direction) and 1 (obstacle edge direction).
(C) Escape target scores over 0.65 are classified as edge vectors; scores under 0.65 are classified as homing vectors (as in Shamash et al.22). Obstacle removal (laser off) vs. open field: p = 0.003; obstacle removal (laser on) vs. open field: p = 0.2; Obstacle removal (laser off) vs. obstacle removal (laser on): p = 0.03, one-tailed permutation tests on proportion of edge-vector escapes.